Synergistic activity of fosfomycin and flucloxacillin against methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: in vitro and in vivo assessment
- PMID: 40544222
- PMCID: PMC12182452
- DOI: 10.1007/s00430-025-00841-3
Synergistic activity of fosfomycin and flucloxacillin against methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: in vitro and in vivo assessment
Abstract
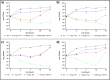
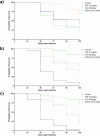
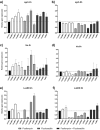
Fosfomycin (FOF) exhibits broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, and is mainly used in combination therapy. Previous in vitro studies have shown synergistic effects of FOF in combination with flucloxacillin (FLX) against Staphylococcus aureus isolates. This study aims to validate these findings in vitro and investigate the synergistic effect in an in vivo Galleria mellonella model. Five methicillin- and FOF-susceptible isolates (ATCC-29213 & 4 clinical isolates); one methicillin- and FOF-resistant strain (DSMZ-23622) and four methicillin-resistant and FOF-susceptible strains (ATCC-33592 & 3 clinical isolates) were tested with checkerboard assays to assess synergism. Time-kill curves were generated for two MSSA (ATCC 29213 and 231/20) and two MRSA strains (ATCC 33592 and DSMZ 23622). The in vivo efficacy of FOF and/or FLX was evaluated by a G. mellonella survival assay and by determining the total bacterial count (TBC) in hemolymph. Checkerboard assays revealed additive or indifferent effects, with some indicating synergism. Time-kill curves demonstrated higher reduction in TBC with combination therapy compared to monotherapy. In vivo, the combination therapy showed the greatest reduction of TBC in larval haemolymph compared to monotherapy, and the survival assay showed highly synergistic activity of FLX plus FOF against MRSA (ATCC-33592) and MSSA (ATCC 6538), resulting in an average reduction in mortality of 48 and 40%, respectively, compared to monotherapies. Therefore, FOF plus FLX could be an alternative for the calculated or definitive treatment of S. aureus infections without antimicrobial susceptibility results or even for salvage therapy of MRSA infections after treatment failure or necessary discontinuation of classical MRSA drugs.
Keywords: Antimicrobial resistance; Combination therapy; Experimental model; In vivo synergy; MRSA.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic antibacterial activity and prevention of drug resistance of daptomycin combined with fosfomycin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025 Aug 6;69(8):e0160924. doi: 10.1128/aac.01609-24. Epub 2025 Jun 18. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025. PMID: 40530996 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of linezolid in monotherapy q12h versus q8h versus combined with daptomycin in the treatment of experimental endocarditis caused by methicillin-resistant and glycopeptide-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus strains.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2025 Jul 1;80(7):1933-1941. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaf149. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2025. PMID: 40424179
-
Antibiotic synergy against Staphylococcus aureus: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025 Aug 6;69(8):e0119924. doi: 10.1128/aac.01199-24. Epub 2025 Jun 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025. PMID: 40526084 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Genomics of Borderline Oxacillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Detected during a Pseudo-outbreak of Methicillin-Resistant S. aureus in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit.mBio. 2022 Feb 22;13(1):e0319621. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03196-21. Epub 2022 Jan 18. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35038924 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for the eradication of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in people with cystic fibrosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 21;7(7):CD009650. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009650.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Dec 13;12:CD009650. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009650.pub5. PMID: 30030966 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA) (2019) Antimicrobial resistance. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory/overview/public-health-thr.... Accessed Nov 28 2019
-
- Ferrara A, Dos Santos C, Cimbro M, Gialdroni GG (1997) Effect of different combinations of sparfloxacin, oxacillin, and fosfomycin against methicillin-resistant staphylococci. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 16:535–537 - PubMed
-
- Noel A, Attwood M, Bowker K, MacGowan A (2020) The pharmacodynamics of fosfomycin against Staphylococcus aureus studied in an in vitro model of infection. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105985 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

