Electrochemotherapy for basal cell carcinoma in the head and neck region: 5-year follow-up from the Insp-ECT registry
- PMID: 40544511
- PMCID: PMC12182940
- DOI: 10.2478/raon-2025-0040
Electrochemotherapy for basal cell carcinoma in the head and neck region: 5-year follow-up from the Insp-ECT registry
Abstract
Background: Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is a cutaneous malignancy that typically appears in sun-exposed areas. We analyzed data from the Insp-ECT registry of all patients affected by BCC in the head and neck region. The aim of this study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of electrochemotherapy (ECT) on a 5-year basis.
Patients and methods: A cohort of 132 patients was included. They were treated by ECT according to the current Standard Operating Procedures. The median age was 74 years (range 41-93). There was a median of 1 nodule per patient (range 1-7), and the median size of the lesions was 1.4 cm (range 0.5-5.0 cm).
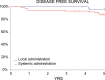
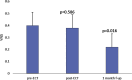
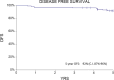
Results: Patients tolerated ECT well, and 96% agreed to repeat it if needed. The side effects were mild and temporary. All patients achieved a complete clinical response after 1 to 3 ECT sessions. During the first year of follow-up, 4 (3%) patients experienced recurrence, which was treated (2 with ECT, 1 with surgery, and 1 with a combination of ECT and surgery), after which they remained free of disease until the end of follow-up at 5 years. Five patients reported recurrence thereafter and were treated according to their condition. At the 5-year follow-up, the disease-free survival (DFS) rate was 92% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 87%-96%). At that time, 3 patients were alive with disease (2%), and 124 patients were free of disease (98%).
Conclusions: This study shows the feasibility and efficacy of ECT treatment in elderly patients with BCC tumors in aesthetically and functionally sensitive areas, with negligible toxicity. Comparable efficacy to other treatment modalities was demonstrated at 1 year and 5 years of follow-up in terms of DFS.
Keywords: 5 years; basal cell carcinoma; electrochemotherapy; recurrence free survival.
© 2025 Ales Groselj et al., published by Sciendo.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Electrochemotherapy for cutaneous Kaposi Sarcoma: A European register-based cohort study from the International Network for Sharing Practices of electrochemotherapy (InspECT).Eur J Surg Oncol. 2025 Aug;51(8):110099. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2025.110099. Epub 2025 Apr 25. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40347711
-
Sun protection for preventing basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jul 25;7(7):CD011161. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011161.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27455163 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
St Andrews Referral Delay in Skin Cancer (StARDISC): a study of keratinocyte skin cancer time to treatment, growth, invasiveness, British Association of Dermatologists risk factors and excision adequacy.Br J Dermatol. 2025 Jun 20;193(1):157-166. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljaf097. Br J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40080699
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
