Unlocking the power of swine gut bacteria: newly isolated Blautia strain and its metabolites inhibit the replication of Salmonella Typhimurium in macrophages and alleviate DSS-induced colitis in mice
- PMID: 40545549
- PMCID: PMC12183824
- DOI: 10.1186/s40104-025-01208-7
Unlocking the power of swine gut bacteria: newly isolated Blautia strain and its metabolites inhibit the replication of Salmonella Typhimurium in macrophages and alleviate DSS-induced colitis in mice
Abstract
Background: Inflammatory bowel disease is a significant health concern for both humans and large-scale farm animals. In the quest for effective alternatives to antibiotics, next-generation probiotics (NGPs) have emerged as a promising option. The genus Blautia presents a rich source of potential NGP strains. Here we successfully isolated Blautia hominis LYH1 strain from the intestines of healthy weaned piglets and characterized its biological traits. Its anti-inflammatory activity was then assessed using macrophages, while its protective effects against colitis and gut barrier damage were validated in a DSS-induced mouse colitis model.
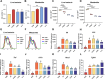
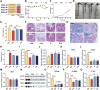
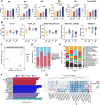
Results: B. hominis LYH1 displayed typical characteristics of an obligate anaerobe, including non-hemolytic and non-motile features, and a genome enriched with carbohydrate-active enzyme genes. It produced metabolites with antibiotic-like compounds, demonstrating antimicrobial activity against Escherichia coli. In vitro, B. hominis LYH1 effectively inhibited pathogen replication in macrophages, reducing cellular infections and alleviating inflammatory damage. In vivo, oral administration of B. hominis LYH1 or its metabolites significantly mitigated DSS-induced colitis in mice by suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines, inhibiting T-lymphocyte activation, and enhancing short-chain fatty acid production.
Conclusions: Our findings underscore B. hominis LYH1's potential as a NGP for maintaining gut health and combating intestinal inflammation. These findings offer valuable insights into the development of antibiotic alternatives and innovative strategies for preventing and treating enteritis in both agricultural and medical settings.
Keywords: Blautia hominis; Colitis; Inflammation; Macrophage.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal procedures used in this study were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Sichuan Agricultural University (license number: CD-SYXK-2017-015). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: There is no conflict of interest between the authors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The mitigative effects of Blautia producta 1009924 on DSS-induced intestinal inflammation.Front Microbiol. 2025 Aug 8;16:1560441. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1560441. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40862149 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro antibacterial efficacy of a novel chicken-derived Bacillus subtilis GX15 strain and its protective mechanisms in mice challenged by Salmonella enterica serovar typhymurium.BMC Microbiol. 2025 Jul 2;25(1):380. doi: 10.1186/s12866-025-04107-z. BMC Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40596838 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Salmonella exploits host- and bacterial-derived β-alanine for replication inside host macrophages.Elife. 2025 Jun 19;13:RP103714. doi: 10.7554/eLife.103714. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40536105 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Liang X, Chen P, Wu X, Xing S, Morais S, He M, et al. Effects of high starch and supplementation of an olive extract on the growth performance, hepatic antioxidant capacity and lipid metabolism of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(3):577. 10.3390/antiox11030577. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Trush EA, Poluektova EA, Beniashvilli AG, Shifrin OS, Poluektov YM, Ivashkin VT. The evolution of human probiotics: challenges and prospects. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2020;12(4):1291–9. 10.1007/s12602-019-09628-4. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

