NIAGADS: A data repository for Alzheimer's disease and related dementia genomics
- PMID: 40545618
- PMCID: PMC12183107
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.70255
NIAGADS: A data repository for Alzheimer's disease and related dementia genomics
Abstract
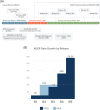
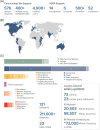
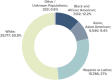
The National Institute on Aging Genetics of Alzheimer's Disease Data Storage Site (NIAGADS) is the National Institute on Aging-designated national data repository for human genetics research on Alzheimer's disease and related dementias (ADRD). NIAGADS maintains a high-quality data collection for ADRD genetic/genomic research and supports genetics data production and analysis, including whole genome and exome sequence data from the Alzheimer's Disease Sequencing Project and other genotype/phenotype data, encompassing 211,000 samples. NIAGADS shares these data with hundreds of research groups around the world via the Data Sharing Service, a Federal Information Security Modernization Act moderate compliant cloud-based platform that fully supports the National Institutes of Health Genomic Data Sharing Policy. NIAGADS Open Access consists of multiple knowledge bases with genome-wide association summary statistics and rich annotations on the biological significance of genetic variants and genes across the human genome. As a one-stop access portal for Alzheimer's disease (AD) genetics, NIAGADS stands as a keystone in promoting collaborations to advance the understanding and treatment of AD. HIGHLIGHTS: The National Institute on Aging Genetics of Alzheimer's Disease Data Storage Site (NIAGADS) is a data repository for the storage of genetics and genomics data. NIAGADS houses data for Alzheimer's disease, related dementias, and healthy aging. NIAGADS offers open and qualified access data and knowledgebases to explore open access data. The Alzheimer's Disease Sequencing Project dataset is the largest Alzheimer's disease and related dementias joint called whole genome sequencing dataset (≈ 58,000 whole genomes).
Keywords: Alzheimer's Disease Sequencing Project; Alzheimer's disease; Alzheimer's disease and related dementias; National Institute on Aging Genetics of Alzheimer's Disease Data Storage Site; bioinformatics; data repository; dementia; genetics; genomics; open access; qualified access; sequencing.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures
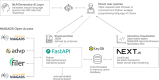
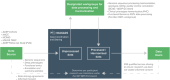
Update of
-
NIAGADS: A Comprehensive National Data Repository for Alzheimer's Disease and Related Dementia Genetics and Genomics Research.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 7:2024.10.07.24315029. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.07.24315029. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Jun;21(6):e70255. doi: 10.1002/alz.70255. PMID: 39417134 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
NIAGADS: A Comprehensive National Data Repository for Alzheimer's Disease and Related Dementia Genetics and Genomics Research.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 7:2024.10.07.24315029. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.07.24315029. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Jun;21(6):e70255. doi: 10.1002/alz.70255. PMID: 39417134 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Alzheimer's Disease Sequencing Project release 4 whole genome sequencing dataset.Alzheimers Dement. 2025 May;21(5):e70237. doi: 10.1002/alz.70237. Alzheimers Dement. 2025. PMID: 40407102 Free PMC article.
-
NIAGADS Alzheimer's GenomicsDB: A resource for exploring Alzheimer's disease genetic and genomic knowledge.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Feb;20(2):1123-1136. doi: 10.1002/alz.13509. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 37881831 Free PMC article.
-
18F PET with florbetapir for the early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 22;11(11):CD012216. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012216.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29164603 Free PMC article.
-
18F PET with flutemetamol for the early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 22;11(11):CD012884. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012884. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29164602 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alzheimer Disease Genetics Consortium . Alzheimer Disease Genetics Consortium . University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine; 2009. Accessed January 31, 2025. https://www.adgenetics.org
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P30 AG013854/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG053760/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AG068082/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072975/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG069013/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG042188/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066444/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102419/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085080/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG064877/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062428/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018016/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG060747/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG023501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG062682/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB015922/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046152/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG029824/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066507/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072946/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG058654/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AG052427/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS017950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066518/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 AG036528/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019771/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG028377/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096812/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG057777/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG063689/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS078086/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG046949/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG042210/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008671/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054076/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG057516/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005142/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG057909/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG058501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG057440/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG052521/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG058922/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AG068053/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG009029/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AG034290/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS069719/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AT000162/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015928/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG044546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS026630/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005128/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG009956/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066511/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG072122/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085082/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG017586/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 TR004407/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066512/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH046373/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K25 AG041906/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG049507/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG057437/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG067501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096917/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG054014/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG052411/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019085/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066515/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG053303/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL130114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046170/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG057907/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG023651/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG048234/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG010483/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG035982/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085083/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54AG052427/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG030146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG043617/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG068057/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG054074/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG067418/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS039764/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066508/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL143790/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008051/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG056270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072978/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG026276/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HG005605/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG058501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG051876/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062429/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096902/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066519/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG007232/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG028786/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR024151/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003273/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG049607/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UF1 AG047133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG057659/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG074855/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054047/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054073/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG061155/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072973/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG049638/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG012300/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG054023/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG025516/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062422/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG054080/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG079280/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG062943/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG051504/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023651/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016573/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047266/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG058066/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG041689/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008017/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG044829/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066462/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG036042/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066530/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG033193/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG025688/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG032990/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG015473/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG026395/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG058589/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS041588/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS080820/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG059716/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG049508/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008012/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS072187/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG052410/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH046290/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096814/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066509/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 AG036547/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG006781/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG041797/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC4 AG039085/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AG068077/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG062602/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS029993/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG047649/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG055477/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AG030944/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG064614/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021547/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG038072/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG032289/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG048927/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG052409/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG033040/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG054052/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG070862/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003079/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG037212/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019757/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG020688/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG022018/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046139/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072977/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG020098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG051125/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG025516/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG064877/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062677/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG052446/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG078109/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070825/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG058654/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 MD000546/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027944/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG010067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072958/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS091856/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025259/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG030653/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047366/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AG068024/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS038377/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003949/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG057519/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062715/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG015473/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG049506/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 NS072026/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 AG011101/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066506/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG058533/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066468/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG041718/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 NS104095/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072947/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG025711/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG058635/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24AG041689/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072931/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072972/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 ES017155/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG072474/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG028383/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG066567/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG017216/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG025204/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072959/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG031272/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025516/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG052525/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS071674/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018023/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UF1 AG051197/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG011380/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG006786/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS100693/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG039700/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072979/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG058267/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG036836/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS055077/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH046281/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG049505/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

