A steep-increasing blood pressure trajectory from early pregnancy is associated with birth outcomes in the EDEN mother-child cohort
- PMID: 40546106
- PMCID: PMC12337948
- DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000004083
A steep-increasing blood pressure trajectory from early pregnancy is associated with birth outcomes in the EDEN mother-child cohort
Abstract
Background: An enhanced consideration of blood pressure (BP) dynamics during pregnancy could improve its monitoring. Distinct BP trajectories may exist, and some have been linked to adverse fetal development. Using maternal BP measurements spanning almost the entire pregnancy, this study aimed to identify trajectories and assess their association with birth outcomes.
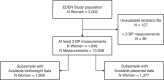
Methods: Routine BP measurements (median = 8) were extracted from the obstetric records of 1849 mothers from the French EDEN birth cohort. Outcomes included birth weight z-score, prematurity and, for a subsample ( n = 1377), placental weight and birth weight-to-placental weight ratio. Maternal SBP trajectories were identified by Latent Class Growth Mixture Modeling. Associations with outcomes were analyzed using adjusted linear or logistic regressions.
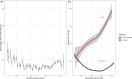
Results: Two BP trajectories were identified: a first U-shaped and a second steep-increasing, comprising 96 and 4% of mothers, respectively. The steep-increasing trajectory reached the hypertensive threshold around 30 weeks of gestation. Over half of mothers in this trajectory had a hypertensive disorder diagnosis, and 24% had preeclampsia. Mothers in this trajectory had newborns with lower birth weight z-scores [β = -0.31, 95% confidence interval (95% CI) = -0.55 to -0.07] and/or increased likelihood of premature delivery (odds ratio = 4.02, 95% CI = 2.04-7.50). No associations were observed with placental outcomes.
Conclusion: Our results suggest the existence of a steep-increasing BP trajectory from the first weeks of pregnancy and associated with poorer birth outcomes. Further investigation into this trajectory's determinants could lead to improved hypertensive disorder risk stratification, ultimately aiding in the prevention of related maternal and fetal consequences.
Keywords: birth cohort; birth weight; blood pressure; hypertension; placenta; pre-eclampsia; pregnancy; risk assessment.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Use of biochemical tests of placental function for improving pregnancy outcome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Nov 25;2015(11):CD011202. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011202.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26602956 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin for women who are overweight or obese during pregnancy for improving maternal and infant outcomes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 24;7(7):CD010564. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010564.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30039871 Free PMC article.
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 6;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 21735394
-
Planned early delivery versus expectant management for hypertensive disorders from 34 weeks gestation to term.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 15;1(1):CD009273. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009273.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28106904 Free PMC article.
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 06;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. PMID: 17253490 Updated.
Cited by
-
Individual and combined effects of maternal per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances exposure on preterm birth: a nested case-control study in China.Environ Health. 2025 Aug 18;24(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12940-025-01213-3. Environ Health. 2025. PMID: 40826094 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khan KS, Wojdyla D, Say L, Gülmezoglu AM, Van Look PF. WHO analysis of causes of maternal death: a systematic review. Lancet 2006; 367:1066–1074. - PubMed
-
- Say L, Chou D, Gemmill A, Tunçalp Ö, Moller A-B, Daniels J, et al. Global causes of maternal death: a WHO systematic analysis. Lancet Glob Health 2014; 2:e323–e333. - PubMed
-
- Sanghavi M, Rutherford JD. Cardiovascular physiology of pregnancy. Circulation 2014; 130:1003–1008. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources