Mitochondrial Regulation of CD8⁺ T Cells: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Modulation
- PMID: 40546111
- PMCID: PMC12407280
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202503095
Mitochondrial Regulation of CD8⁺ T Cells: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Modulation
Abstract
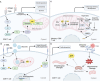
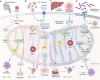
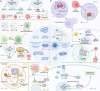
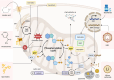
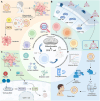
Mitochondria are integral to the regulation of CD8+ T cell function, critically influencing processes such as activation, differentiation, and long-term persistence during immune responses. Emerging evidence highlights the detrimental impact of mitochondrial dysfunction on CD8+ T cell activity, contributing to immune exhaustion and impairing both antitumor and antiviral immunity. This underscores the importance of understanding and modulating mitochondrial dynamics to optimize T cell-based immunotherapies. In this review, a comprehensive and in-depth analysis of the essential mitochondrial processes-including biogenesis, redox homeostasis, and metabolic reprogramming is provided-that govern CD8+ T cell function and are intricately linked to their therapeutic potential. The current strategies aimed at enhancing mitochondrial function in CD8+ T cells are also examined, focusing on both metabolic reprogramming and mitochondrial-targeted interventions. Despite these promising approaches, several significant challenges remain, such as achieving selective targeting, addressing mitochondrial plasticity, and mitigating off-target effects. Overcoming these obstacles will be crucial to improving the clinical efficacy and safety of mitochondrial modulation therapies. As the understanding of mitochondrial dynamics within CD8+ T cells continues to evolve, there is growing potential to leverage these insights to improve immune-based therapies across a range of diseases, including cancer and viral infections.
Keywords: CD8⁺ T cells; T cell exhaustion; immunotherapy; metabolic reprogramming; mitochondrial dynamics.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
The mechanisms and clinical significance of CD8+ T cell exhaustion in anti-tumor immunity.Cancer Biol Med. 2025 Jun 10;22(5):460-80. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2024.0628. Cancer Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 40492696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[CD8+ T Cells in Anti-Tumor Immune Response].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2025 Jul;52(7):485-491. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2025. PMID: 40840892 Review. Japanese.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Mitochondrial dynamics dysfunction and neurodevelopmental disorders: From pathological mechanisms to clinical translation.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Jun 19. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-01422. Online ahead of print. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 40537021
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2022A0505050038/Guangdong Provincial Science and Technology Project Foundation
- 81901006 82372905/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 0920220228/Young Top-notch Talent of Pearl River Talent Plan
- 2025A04J3464/Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou
- RC202005/Scientific Research Talent Cultivation Project of Stomatological Hospital, Southern Medical University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
