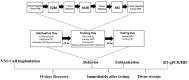
Vagus nerve stimulation ameliorates cognitive impairment caused by hypoxia
- PMID: 40546247
- PMCID: PMC12179086
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2025.1555229
Vagus nerve stimulation ameliorates cognitive impairment caused by hypoxia
Abstract
Introduction: Hypoxia significantly impairs cognitive function due to the brain's high demand for oxygen. While emerging evidence suggests that vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) can enhance cognition, its effectiveness in mitigating behavioral and molecular impairments caused by hypoxia remains unknown. This study investigated whether VNS could alleviate hypoxia-induced deficits in cognitive performance and neurotrophin expression in rats.
Methods: Healthy male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly assigned to three groups: sham, hypoxia, and VNS + hypoxia. VNS was delivered during hypoxia (8% oxygen) exposure using 100 μs biphasic pulses at 30 Hz and 0.8 mA. Cognition and performance were assessed by behavioral testing and hippocampal tissue was collected for molecular analysis. NGF and BDNF mRNA levels were measured by quantitative PCR, and protein expression was evaluated by immunohistochemistry.
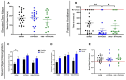
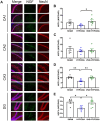
Results: The passive avoidance test (PAT) performance was significantly reduced by hypoxia exposure compared to the sham group, and administration of VNS during hypoxia ameliorated this impairment. Hypoxia significantly reduced NGF and BDNF mRNA levels in the hippocampus 24 h post-exposure. VNS restored NGF mRNA to sham levels and partially increased BDNF mRNA. Immunohistochemistry results showed VNS significantly restored NGF protein expression in the hippocampus, while BDNF levels remained unchanged.
Discussion: These findings suggest that VNS may serve as a promising intervention for cognitive impairments induced by hypoxia.
Keywords: BDNF; NGF; hypoxia; learning; memory; rats; vagus nerve stimulation.
Copyright © 2025 Sharma, Jones, Olsen, Moore, Curtner and Hatcher-Solis.
Conflict of interest statement
BS, KJ, LO, RM, and FC are employed by corporations that supply contractor labor support to the U.S. federal government. The corporations or employees have no financial interest in the outcome of this research. BS and LO were fellowship participants with Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education. KJ was employed by UES, Inc., BlueHalo. RM and FC were employed by DCS Infoscitex. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vagus nerve stimulation ameliorates learning-memory deficits and suppresses neuronal apoptosis via the ERK/CREB/BDNF signaling pathway in epileptic rats.Int J Neurosci. 2025 Aug 9:1-11. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2025.2542882. Online ahead of print. Int J Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40757650
-
Vagus nerve stimulation for focal seizures.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 14;7(7):CD002896. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002896.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35833911 Free PMC article.
-
Abdominal Vagus Nerve Stimulation Increases Firing in the Rat Locus Coeruleus.Neuromodulation. 2025 Jun 20:S1094-7159(25)00188-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neurom.2025.05.003. Online ahead of print. Neuromodulation. 2025. PMID: 40542812
-
Vagus Nerve Stimulation Inhibits DNA and RNA Methylation in a Rat Model of Pilocarpine-Induced Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Jun;31(6):e70484. doi: 10.1111/cns.70484. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40534269 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Vagus Nerve Stimulation on Attention and Working Memory in Neuropsychiatric Disorders: A Systematic Review.Neuromodulation. 2022 Apr;25(3):343-355. doi: 10.1016/j.neurom.2021.11.009. Epub 2022 Jan 26. Neuromodulation. 2022. PMID: 35088719
References
-
- Alvarez-Dieppa A. C., Griffin K., Cavalier S., Souza R. R., Engineer C. T., McIntyre C. K. (2025). Vagus nerve stimulation rescues impaired fear extinction and social interaction in a rat model of autism spectrum disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 374, 505–512. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2025.01.098, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

