Global, regional, and national burdens and trends of migraine among males aged 10-59 years from 1990 to 2021: insights from the Global Burden of Disease study 2021
- PMID: 40546260
- PMCID: PMC12178871
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1585512
Global, regional, and national burdens and trends of migraine among males aged 10-59 years from 1990 to 2021: insights from the Global Burden of Disease study 2021
Abstract
Background: Migraine, a prevalent neurological disorder, significantly impacts quality of life across populations. Although various demographic groups are impacted, existing research has focused predominantly on the general population, women, and adolescents, with insufficient emphasis on the burden experienced by men. This study aims to analyze data from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study spanning from 1990 to 2021, with the objective of elucidating the global prevalence, incidence, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) associated with migraine in males aged 10-59 years. Our investigation seeks to provide insights into this underexplored aspect of migraine's impact over three decades. Epidemiological Transition refers to a shift in the burden of disease from communicable diseases to chronic non-communicable diseases, which in this study is reflected in the rising relative burden of migraine among men. Secondary Prevention (Secondary Prevention) reduces the frequency of migraine attacks through early diagnosis and intervention, e.g., use of prophylactic medications; Tertiary Prevention (Tertiary Prevention): reduces the degree of disability in diagnosed patients, e.g., cognitive-behavioral therapy.
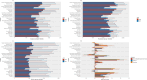
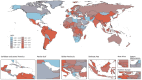
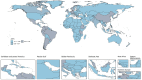
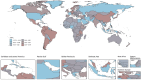
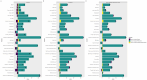
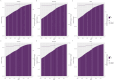
Results: From 1990 to 2021, there was a significant increase in the burden of migraine among males aged 10-59 years worldwide. The number of incident cases rose by 46.55%, the number of prevalent cases rose by 56.54%, and the number of DALYs increased by 56.95%. The middle-SDI region showed the fastest burden growth. At the country level, Belgium had the highest prevalence and DALYs, whereas Indonesia and the Philippines had the highest incidence. Age-period-cohort analysis revealed a peak incidence in the 10-14 years age group, with the prevalence and DALYs peaking in the 30-44 years age range. Population growth was the primary driver of increased burdens in most regions. Projections suggest a continued increase in migraine burden among this population in the future.
Conclusion: This paper is the first to systematically analyze the age-period-cohort effect of migraine in men and to reveal a unique upward trend in the burden of migraine among men in the high-income Asia-Pacific region (in contrast to the trend among women). From 1990 to 2021, the migraine burden among males aged 10-59 years has generally increased and is expected to continue rising. Notably, the incidence is highest among adolescents (10-14 years), whereas the prevalence and DALYs peak in the middle-aged group (30-44 years). To address this, we should focus on primary prevention in adolescents and implement secondary and tertiary prevention strategies for the middle-aged population to reduce the overall migraine burden in males. Additionally, in the high-income Asia-Pacific region, the increasing trend in migraine burden differs from previous research findings.
Keywords: GBD 2021; disease burden; epidemiology; migraine; sex differences.
Copyright © 2025 Zhao, Wang, Chen and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Burden of knee osteoarthritis in China and globally: 1990-2045.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Jul 1;26(1):582. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08858-8. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40598022 Free PMC article.
-
Global trends in testicular and prostate cancer among adolescents and young adult males aged 15-49 years, 1990-2021: insights from the GBD study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23388. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07361-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40603429 Free PMC article.
-
Global pattern, trend and cross-country inequalities of inguinal, femoral, and abdominal hernia among individuals aged 60 and above from 1990 to 2021 and projections until 2040: a population-based study.Surg Endosc. 2025 Jul;39(7):4335-4344. doi: 10.1007/s00464-025-11810-5. Epub 2025 May 28. Surg Endosc. 2025. PMID: 40437076
-
Behavioral interventions to reduce risk for sexual transmission of HIV among men who have sex with men.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD001230. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001230.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. PMID: 18646068
-
Burden of inflammatory bowel disease among elderly, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis based on the global burden of disease study 2019.Autoimmun Rev. 2025 Jan 31;24(2):103708. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2024.103708. Epub 2024 Nov 23. Autoimmun Rev. 2025. PMID: 39586389
References
-
- Li X, Yang CH, Lv JJ, Liu H, Zhang LY, Yin MY, et al. Global, regional, and national epidemiology of migraine and tension-type headache in youths and young adults aged 15–39 years from 1990 to 2019: findings from the global burden of disease study 2019. J Headache Pain. (2023) 24:126. doi: 10.1186/s10194-023-01659-1, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

