Inadvertent intrathecal application of vindesine and its neurological outcome: case report and systematic review of the literature
- PMID: 40546273
- PMCID: PMC12179714
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bas.2025.104292
Inadvertent intrathecal application of vindesine and its neurological outcome: case report and systematic review of the literature
Abstract
Introduction: Vinca alkaloids are used to treat a diversity of malignancies. Inadvertent intrathecal application is followed by severe neurological consequences, with fatal outcomes in the majority of the reported cases. Therapy of choice has been experimental.
Research question: What are the outcomes of inadvertent intrathecal application of vinca alkaloids and how should it be treated? What is the role of irrigation of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in order to remove the vinca alkaloid and potentially toxic metabolites?
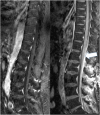
Material and methods: In this paper we report the case of a 53-year-old man who was, in the course of his treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), inadvertently injected with vindesine intrathecally. The patient survived following aggressive and invasive treatment, which included irrigation of the CSF via external ventricular and lumbar drains. We also conducted a systematic review of similar published cases.
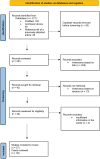
Result: A total of 31 cases with intrathecal inadvertent vinca alkaloid injection were identified. Including the case described in this report only two patients were injected with vindesine (n = 2, 6.5 %), all other received vincristine. Only 6/31 (19.4 %) patients survived the acute phase of the vinca alkaloid intoxication. 6/15 (40.0 %) patients receiving some sort of CSF irrigation survived (cf. 0/12 without irrigation therapy). All survivors were left with very significant neurological deficits.
Discussion and conclusion: The combined evidence suggests that intrathecal administration of vincristine is universally fatal without treatment, while CSF irrigation carries a chance of survival. Patients are, however, left with severe neurological deficits such as paraplegia.
Keywords: Case report; Intrathecal; Vincristine; inadvertent; vindesine.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

