17β-estradiol maintains extracellular matrix homeostasis of nucleus pulposus cells by activating p70 S6K1 signaling pathway
- PMID: 40546320
- PMCID: PMC12179197
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1564458
17β-estradiol maintains extracellular matrix homeostasis of nucleus pulposus cells by activating p70 S6K1 signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Estrogen can inhibit the apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells (NPCs) through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. However, the downstream of mTOR signaling pathway remains elusive. This study investigates the effect of 17β-estradiol (E2) on intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD) through the p70 S6K1 signaling pathway, downstream of mTOR.
Methods: The IVDD model of rats was established by needle puncture and bilateral ovariectomy. Fifteen Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly assigned to the following three groups: (A) Sham surgery group (Sham); (B) Bilateral ovariectomy, 21G needle puncture and carrier injection (OVX + veh); (C) Bilateral ovariectomy, 21G needle puncture, E2 supplementation (OVX + E2). The degree of IVDD was evaluated by X-ray, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), and Safranin O-Fast Green staining. The expression levels of target protein p70S6K1 and its phosphorylated products were detected by immunohistochemistry (IHC). Finally, Western blot analysis and immunofluorescence staining were used to investigate the effect of E2 on the p70 S6K1 signaling pathway in vitro.
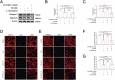
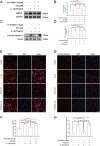
Results: Histological staining and radiological results showed that E2 supplementation altered signaling, suggesting that it may have a protective effect against IVDD. IHC showed that compared with the Sham and OVX + E2 groups, the level of p70 S6K1 in the OVX + veh group was significantly increased while the expression of phosphorylated products (p-S6) was significantly decreased, suggesting that E2 could inhibit IVDD by activating p70 S6K1 signaling pathway, the downstream of mTOR. Furthermore, cellular immunofluorescence and Western blot showed that E2 can maintain extracellular matrix (ECM) balance and inhibits apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells (NPCs) by activating the p70 S6K1 signaling pathway.
Conclusion: In summary, 17β-estradiol mitigates IVDD progression by maintaining ECM homeostasis and inhibiting NPCs apoptosis through activation of the p70 S6K1 signaling pathway downstream of mTOR.
Keywords: P70 S6K1; apoptosis; estradiol; intervertebral disc degeneration; mTOR; nucleus pulposus.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Li, Zhang, Guo, Liu, Yang and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures




References
-
- Chen J., Xuan J., Gu Y., Shi K. S., Xie J. J., et al. (2017). Celastrol reduces il-1β induced matrix catabolism, oxidative stress and inflammation in human nucleus pulposus cells and attenuates rat intervertebral disc degeneration in vivo . Biomed. Pharmacother. 91, 208–219. 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.04.093 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

