A Comprehensive Survey of Brain-Computer Interface Technology in Health care: Research Perspectives
- PMID: 40546334
- PMCID: PMC12180781
- DOI: 10.4103/jmss.jmss_49_24
A Comprehensive Survey of Brain-Computer Interface Technology in Health care: Research Perspectives
Abstract
The brain-computer interface (BCI) technology has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation with profound implications across diverse domains, particularly in health care. By establishing a direct communication pathway between the human brain and external devices, BCI systems offer unprecedented opportunities for diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation, thereby reshaping the landscape of medical practice. However, despite its immense potential, the widespread adoption of BCI technology in clinical settings faces several challenges. These include the need for robust signal acquisition and processing techniques and optimizing user training and adaptation. Overcoming these challenges is crucial to unleashing the complete potential of BCI technology in health care and realizing its promise of personalized, patient-centric care. This review work underscores the transformative potential of BCI technology in revolutionizing medical practice. This paper offers a comprehensive analysis of medical-oriented BCI applications by exploring the various uses of BCI technology and its potential to transform patient care.
Keywords: Alzheimer; brain-computer interface; human-computer interaction; neurofeedback; prosthetic control.
Copyright: © 2025 Journal of Medical Signals & Sensors.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Systematic Review of Virtual Reality and Robot Therapy as Recent Rehabilitation Technologies Using EEG-Brain-Computer Interface Based on Movement-Related Cortical Potentials.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Dec 6;12(12):1134. doi: 10.3390/bios12121134. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551100 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive Electroencephalography Equipment for Assistive, Adaptive, and Rehabilitative Brain-Computer Interfaces: A Systematic Literature Review.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Jul 12;21(14):4754. doi: 10.3390/s21144754. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34300492 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Electroencephalography Brain-Computer Interface Systems as a Rehabilitative Approach for Upper Limb Function After a Stroke: A Systematic Review.PM R. 2017 Sep;9(9):918-932. doi: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2017.04.016. Epub 2017 May 13. PM R. 2017. PMID: 28512066
-
How lived experiences of illness trajectories, burdens of treatment, and social inequalities shape service user and caregiver participation in health and social care: a theory-informed qualitative evidence synthesis.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025 Jun;13(24):1-120. doi: 10.3310/HGTQ8159. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025. PMID: 40548558
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
References
-
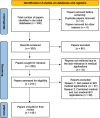
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151:264–9. - PubMed
-
- Tian Z. International Conference on Mathematics, Modeling, and Computer Science (MMCS2022) Vol. 12625. SPIE; 2023. Research on the relationship between brain signal analysis algorithm and invasive brain computer interface; pp. 442–8.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources