Comprehensive Analysis of Differences in N6-Methyladenosine RNA Methylation Groups in CVB3-Induced Viral Myocarditis and Identification of the Anti-Apoptotic Role of RBM15B
- PMID: 40546402
- PMCID: PMC12182079
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S503823
Comprehensive Analysis of Differences in N6-Methyladenosine RNA Methylation Groups in CVB3-Induced Viral Myocarditis and Identification of the Anti-Apoptotic Role of RBM15B
Abstract
Background: Viral myocarditis (VMC) is a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in children and young adults, with Coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3) identified as the primary viral pathogen responsible. N6-methyladenosine (m6A), the most abundant and reversible RNA methylation modification in mammals, plays a pivotal role in regulating numerous biological processes. However, the potential effects of CVB3 infection on m6A methylation within the myocardium remain unexplored. In this study, we investigated alterations in global RNA m6A methylation levels during CVB3 infection using both in vitro and in vivo models, and further examined the regulatory role of the m6A methyltransferase RBM15B in vitro.
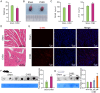
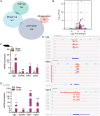
Methods: First, the total quantity of m6A was quantified in Balb/c mice and HL-1 cells with CVB3 infection via m6A dot blot analysis. Subsequently, m6A methylation sequencing (MeRIP-seq) and RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) were performed on cell model, while RNA-seq was conducted on animal tissues. We further analyzed the expression of m6A regulatory genes and their involvement in key pathways linked to VMC pathogenesis to elucidate underlying mechanisms. Given the pronounced expression of RBM15B in vitro, we knocked down RBM15B and assessed its regulatory effects on CVB3-infected HL-1 cells using Western blotting, viral plaque assays, and Calcein AM/PI double staining.
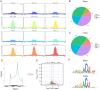
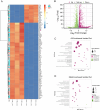
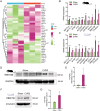
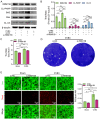
Results: Quantitative m6A analysis revealed elevated m6A modification levels in CVB3 infection group. MeRIP-seq identified 327 significantly altered m6A peaks (116 upregulated, 211 downregulated). RNA-seq detected 1,597 upregulated and 2,942 downregulated mRNAs. Integrated analysis of MeRIP-seq and RNA-seq identified 38 hypermethylated-upregulated, 23 hypermethylated-downregulated, 65 hypomethylated-downregulated, and 13 hypomethylated-upregulated genes. GO and KEGG pathway analyses of these differentially methylated genes highlighted their roles in broad biological functions. Furthermore, qRT-PCR validation of mice RNA-seq data confirmed significant differences in four key genes (Igtp, ApoI9b, Ddit3, and Irgm3), along with altered expression of m6A regulators (IGF2BP2, EIF3H, RBM15B, and YTHDC2), with RBM15B showing the most pronounced changes. RBM15B knockdown in HL-1 cells reduced CVB3 replication (viral plaque assay) and attenuated apoptosis induced by CVB3 infection (Calcein AM/PI staining and Western blotting).
Conclusion: These findings establish a foundation for exploring the role of m6A methylation in CVB3-associated VMC and may provide novel therapeutic insights for managing CVB3-induced viral myocarditis.
Keywords: HL-1 cell; RBM15B; apoptosis; coxsackievirus B3; m6A; viral myocarditis.
© 2025 Hu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
N6-methyladenosine RNA landscape in the aged mouse hearts.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jun 18;12:1563364. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1563364. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40606020 Free PMC article.
-
m6A-related bioinformatics analysis and functional characterization reveals that METTL3-mediated NPC1L1 mRNA hypermethylation facilitates progression of atherosclerosis via inactivation of the MAPK pathway.Inflamm Res. 2023 Mar;72(3):429-442. doi: 10.1007/s00011-022-01681-0. Epub 2022 Dec 30. Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 36583755
-
Transcriptome-wide N6-methyladenosinem modifications analysis of chicken cecum in responding to Campylobacter jejuni inoculation.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 30;16:1630008. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1630008. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40808945 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Kwong JS. Herbal medicines for viral myocarditis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;11:CD003711. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

