The Combined Diagnostic Value of Serum Trefoil Factor 2 and microRNA-186-5p for Evaluating Disease Severity in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis
- PMID: 40546405
- PMCID: PMC12182058
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S527630
The Combined Diagnostic Value of Serum Trefoil Factor 2 and microRNA-186-5p for Evaluating Disease Severity in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis
Abstract
Objective: This study investigated the association of serum Trefoil Factor 2 (TFF2) and microRNA-186-5p (miR-186-5p) levels with the severity and prognosis of acute pancreatitis (AP).
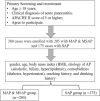
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 380 AP patients, classified into mild to moderately severe (mild acute pancreatitis (MAP) and moderately severe acute pancreatitis (MSAP), n=205) and severe (SAP, n=175) groups. Serum TFF2 levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and miR-186-5p expression was quantified via reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). Correlations with inflammatory markers (high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), interleukin-18 (IL-18), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)) and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II) scores were assessed using Pearson analysis. Diagnostic performance was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, and logistic regression was used to identify risk factors for SAP.
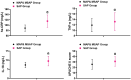
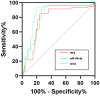
Results: Compared with the MAP&MSAP group, the SAP group showed significantly elevated TFF2, hs-CRP, IL-18, TNF-α levels, and APACHE II scores, while miR-186-5p levels were significantly reduced (P < 0.05). TFF2 levels were positively correlated with inflammatory markers and APACHE II scores (r = 0.427-0.546), whereas miR-186-5p levels showed negative correlations (r = -0.431 to -0.570; all P < 0.05). TFF2 and miR-186-5p levels were inversely correlated (r = -0.483, P < 0.05). ROC analysis yielded AUCs of 0.804 for TFF2, 0.832 for miR-186-5p, and 0.895 for their combination in predicting SAP. Logistic regression identified TFF2 as an independent risk factor and miR-186-5p as a protective factor for SAP (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Elevated serum TFF2 level and reduced miR-186-5p level were found to be associated with increased AP severity. These biomarkers may serve as useful indicators for assessing disease severity and prognosis in AP.
Keywords: acute pancreatitis; disease severity; miR-186-5p; prognosis; relationship; serum TFF2.
© 2025 Fang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

