Risk Factors of Non-Classic Radiation-Induced Liver Disease (ncRILD) After Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 40546439
- PMCID: PMC12182741
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S539527
Risk Factors of Non-Classic Radiation-Induced Liver Disease (ncRILD) After Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to identify independent risk factors for non-classic radiation-induced liver disease (ncRILD) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients treated with intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and to construct a predictive nomogram.
Patients and methods: We retrospectively analyzed 177 primary HCC patients treated with IMRT between 2013 and 2021. Univariate and multivariate analyses were conducted to identify risk factors for ncRILD. A nomogram was developed based on significant variables. Dosimetric parameters were also assessed across different fractionation doses.
Results: Multivariate analysis identified tumor number ≥ 2, mean liver dose ≥ 1371.4 cGy, and normal liver volume < 700 mL as independent risk factors for ncRILD. A nomogram was established using logistic regression. In patients receiving ≥ 4 Gy per fraction, ncRILD was significantly associated with Vs5-Vs40 (p < 0.05), but not with V5-V40. No such associations were found for 2 Gy and 3 Gy groups.
Conclusion: Patients with multifocal tumor, lower normal liver volume and higher mean liver dose are at increased risk of developing radiation-induced liver injury. These findings suggest that dosimetric parameters, especially at higher fraction doses, may play a critical role in the occurrence of ncRILD.
Keywords: IMRT; child-Pugh score; hepatocellular carcinoma; liver toxicity; ncRILD.
© 2025 Du et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests in this work.
Figures

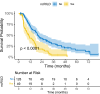


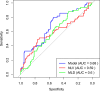
References
-
- Zhu AX, Kang Y-K, Yen C-J, et al. Ramucirumab after sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and increased α-fetoprotein concentrations (REACH-2): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(2):282–296. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30937-9 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Qin S, Li Q, Gu S, et al. Apatinib as second-line or later therapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (AHELP): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;6(7):559–568. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00109-6 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

