The Impact of Triglyceride-Glucose Index on Carotid Atherosclerosis: A Prospective Cohort Study in Middle Aged and Elderly Low-Income in Rural Chinese
- PMID: 40546456
- PMCID: PMC12182086
- DOI: 10.2147/RMHP.S522995
The Impact of Triglyceride-Glucose Index on Carotid Atherosclerosis: A Prospective Cohort Study in Middle Aged and Elderly Low-Income in Rural Chinese
Abstract
Background: Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) is a major global health burden. The triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index, as a surrogate marker of insulin resistance, is associated with atherosclerosis, but its role in predicting carotid plaque and intima-media thickness (IMT) changes remains unclear. This study aimed to assess the relationship between the TyG index and carotid plaque incidence and IMT changes over a six-year period in a cohort of middle-aged and elderly individuals with low income and low education in rural China.
Methods: The study was conducted from 2014 to 2020 in 18 rural villages in Tianjin, China. A total of 2702 participants were included in the IMT analysis, and after excluding those with carotid plaques at baseline, 1595 participants were included in the plaque incidence analysis. Multivariate logistic regression was used to assess the relationship between the TyG index and outcomes. Subgroup analyses were based on significant indicators from the multivariate adjustment.
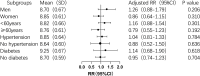
Results: During the six-year follow-up, 551 new cases of carotid plaque were identified, with an incidence rate of 34.5%. Univariate analysis showed a significant association between the TyG index and increased plaque incidence. However, after adjusting for multiple confounders, the TyG index emerged as an independent predictor only for IMT increase. Each 1-unit increase in TyG was associated with a 49% increased risk (RR: 1.49; 95% CI: 1.05-2.13; P = 0.026), with this association being particularly strong in males, individuals aged ≥60 years, and those without hypertension.
Conclusion: Results highlight the importance of incorporating the TyG index into cardiovascular risk assessments, especially for IMT changes in specific subpopulations. The study underscores the need for targeted prevention strategies in rural, low-education and low-income populations. Future research is needed to elucidate the potential interactions between the TyG index and other metabolic factors in ASCVD.
Keywords: cardiovascular risk factors; carotid plaque; intima-media thickness; rural populations; triglyceride-glucose index.
© 2025 Meng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A retrospective cross-sectional study of association between triglyceride-glucose index and carotid atherosclerosis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jun 6;12:1611466. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1611466. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40547502 Free PMC article.
-
TyG-BMI as a predictor of ischemic stroke over 10 years in middle-aged and older adults: findings from the China cardiometabolic disease and cancer cohort (4C) study.Front Neurol. 2025 Jul 2;16:1609853. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1609853. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40672456 Free PMC article.
-
[Association Between Surrogate Markers of Insulin Resistance and Incident Cardiovascular Disease in a Population With Stages 0-3 Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome: A Prospective Cohort Study].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 Mar 20;56(2):495-505. doi: 10.12182/20250360503. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40599269 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
The triglyceride-glucose index: updating evidence from clinical settings to molecular mechanisms in ageing-related cerebrovascular diseases.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Aug 26;24(1):350. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02914-2. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40859224 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- GBD 2021 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet. 2024;403(10440):2133–2161. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00757-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

