An Incidental Discovery of Dandy-Walker Malformation on MRI in a 76-Year-Old Male Patient: A Case Report
- PMID: 40546618
- PMCID: PMC12178834
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.84423
An Incidental Discovery of Dandy-Walker Malformation on MRI in a 76-Year-Old Male Patient: A Case Report
Abstract
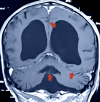
Dandy-Walker malformation is the most prevalent posterior fossa anomaly. Dandy-Walker variant, or Dandy-Walker complex, are terms devised to contrast those conditions that do not meet the standard of Dandy-Walker malformation. Dandy-Walker malformation is usually a congenital diagnosis. Our case calls attention to an extraordinary presentation of Dandy-Walker malformation in adulthood. A 76-year-old male patient initially presented to the Emergency Department at Dow University Hospital at Ojha Campus on the grounds of suspicion of a respiratory infection. COVID-19 was suspected; however, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing yielded a negative result. The patient later developed an erythematous and swollen left arm, which pointed towards a diagnosis of cellulitis, and the patient was managed accordingly. After being moved to the General Medicine Ward, our team noted that the patient was bed-bound and conducted a neurological exam, in which he presented with incoordination, less brisk and pendular deep tendon reflexes, and hypotonia in lower limbs, all suggestive of cerebellar involvement. The patient was also lethargic and was in a state of confusion, suggesting an altered mental status. Subsequent labs were completed, and bacterial pneumonia was confirmed on pleural fluid analysis. A CT scan of the head and an MRI scan of the brain were also ordered to investigate the reason for neurological involvement. The imaging displayed hallmarks signifying Dandy-Walker malformation, such as enlargement of the fourth ventricle, hypoplastic vermis, and posterior fossa anomalies.
Keywords: adult; aged; ataxia; cerebellum; dandy-walker syndrome; incidental findings; magnetic resonance imaging; male.
Copyright © 2025, Ahmad et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(45):iii-iv, ix-221. doi: 10.3310/hta11450. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999840
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Interventions for promoting habitual exercise in people living with and beyond cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Sep 19;9(9):CD010192. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010192.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30229557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dandy-Walker malformation: an incidental finding. Tadakamadla J, Kumar S, Mamatha GP. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2927792/ Indian J Hum Genet. 2010;16:33–35. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Isolated posterior fossa hypertension and brainstem compression caused by entrapped Dandy-Walker cyst: a case report. Rahman NU, Jamjoom A, Jamjoom ZAB. https://www.archive.jpma.org.pk/article-details/4581. J Pak Med Assoc. 1995;45:190–191. - PubMed
-
- Dandy-Walker malformation: a clinical and surgical outcome analysis. Bokhari I, Rehman L, Hassan S, Sattar Hashim M. https://www.jcpsp.pk/archive/2015/Jun2015/10.pdf. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2015;25:431–433. - PubMed
-
- Jansen AC, Keymolen K. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Vol. 162. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier B.V.; 2019. Fetal and neonatal neurogenetics; pp. 105–132. - PubMed
-
- Old age presentation of the Dandy-Walker syndrome associated with unilateral sudden sensorineural deafness and vertigo. Freeman SR, Jones PH. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11827588/ J Laryngol Otol. 2002;116:127–131. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
