Biomarkers for tracking metabolic changes pre-post nutritional epigenetics diet/intervention to prevent autism and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorders in children
- PMID: 40546679
- PMCID: PMC12019618
- DOI: 10.5493/wjem.v15.i2.101555
Biomarkers for tracking metabolic changes pre-post nutritional epigenetics diet/intervention to prevent autism and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorders in children
Abstract
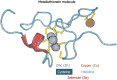
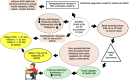
The prevalence of autism and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorders is increasing worldwide. Recent studies suggest the excessive intake of ultra-processed food plays a role in the inheritance of these disorders via heavy metal exposures and nutritional deficits that impact the expression of genes. In the case of the metallothionein (MT) gene, biomarker studies show dietary zinc (Zn) deficits impact MT protein levels in children with autism and are associated with the bioaccumulation of lead and/or mercury in children exhibiting autism/attention deficit/hyperactivity disorders symptomology. The impact of dietary changes on lead and mercury exposures and MT gene behavior could be determined using a randomized test and control group design. Pregnant women serving in the test-group would participate in a nutritional epigenetics education intervention/course designed to reduce ultra-processed food intake and heavy metal levels in blood while increasing whole food intake and MT and Zn levels. Changes in maternal diet would be measured using data derived from an online diet survey administered to the test and control groups pre-post intervention. Changes in maternal lead, mercury, Zn, and MT levels would be measured via blood sample analyses prior to the intervention and after childbirth via cord blood analyses to determine infant risk factors.
Keywords: Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder; Autism; Lead; Mercury; Metallothionein; Nutritional epigenetics; Zinc.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The author reports no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Atypical antipsychotics for disruptive behaviour disorders in children and youths.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Aug 9;8(8):CD008559. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008559.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28791693 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for preventing eating disorders in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;2002(2):CD002891. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002891. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002. PMID: 12076457 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological and/or educational interventions for the prevention of depression in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(1):CD003380. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003380.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Dec 07;(12):CD003380. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003380.pub3. PMID: 14974014 Updated.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis links autism and toxic metals and highlights the impact of country development status: Higher blood and erythrocyte levels for mercury and lead, and higher hair antimony, cadmium, lead, and mercury.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2017 Oct 3;79(Pt B):340-368. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.07.011. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28716727
-
Calcium supplementation commencing before or early in pregnancy, or food fortification with calcium, for preventing hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 26;9(9):CD011192. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011192.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Sep 16;9:CD011192. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011192.pub3. PMID: 28949421 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Cooper M. Reducing special education costs by providing early intervention for autistic children. Behav Intervent. 2022;37:397–414.
-
- United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Autism Spectrum Disorder. May 16, 2024. [cited 19 September 2024] Available from https://www.cdc.gov/autism/signs-symptoms/index.html .
-
- Maenner MJ, Warren Z, Williams AR, Amoakohene E, Bakian AV, Bilder DA, Durkin MS, Fitzgerald RT, Furnier SM, Hughes MM, Ladd-Acosta CM, McArthur D, Pas ET, Salinas A, Vehorn A, Williams S, Esler A, Grzybowski A, Hall-Lande J, Nguyen RHN, Pierce K, Zahorodny W, Hudson A, Hallas L, Mancilla KC, Patrick M, Shenouda J, Sidwell K, DiRienzo M, Gutierrez J, Spivey MH, Lopez M, Pettygrove S, Schwenk YD, Washington A, Shaw KA. Prevalence and Characteristics of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years - Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2020. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2023;72:1–14. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

