The triple-plane technique: a surgical technique for subpectoral implant-based breast reconstruction
- PMID: 40546844
- PMCID: PMC12177546
- DOI: 10.21037/gs-2025-116
The triple-plane technique: a surgical technique for subpectoral implant-based breast reconstruction
Abstract
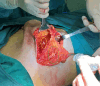
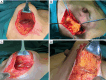
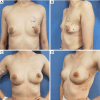
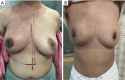
Breast reconstruction surgery is an important part of breast cancer treatment. However, implant-based breast reconstruction is associated with a number of complications, such as infection, seroma, prosthesis exposure, and skin erythema. In this study, we propose a novel surgical technique for implant-based breast reconstruction-the triple-plane technique. This technique positions the prosthesis in a complete submuscular plane. Medially, it is subpectoral, and inferolaterally it is covered by a flap of serratus anterior and latissimus dorsi fascia. As such, the prosthesis is not in contact with the skin, thereby reducing postoperative complications. This article reports on the breast reconstruction results of 96 breast cancer patients who underwent unilateral breast reconstruction surgery using the triple-plane technique at Hunan Cancer Hospital. The results show that breast appearance after surgery was rated as excellent by 92 (95.83%) patients, and good by 4 (4.17%) patients. The average operation time, surgical incision, intraoperative blood loss, and hospitalization time of patients were 88.40±12.13 minutes, 12.24±4.01 cm, 46.40±10.73 mL, and 7.23±1.00 days, respectively. Skin necrosis at the edge of the incision was observed in 1 (1.04%) patient, which healed normally after debridement and closure. The scores of BREAST-Q patient-reported outcome measure ranged from 80 to 100 points for all of the patients. These results demonstrate that the triple-plane technique offers a novel and safe technique for breast reconstruction surgery.
Keywords: Breast reconstruction; postoperative complications; prosthesis implantation.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://gs.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/gs-2025-116/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Single-incision sling operations for urinary incontinence in women.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 26;7(7):CD008709. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008709.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Oct 27;10:CD008709. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008709.pub4. PMID: 28746980 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Coblation versus other surgical techniques for tonsillectomy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Aug 22;8(8):CD004619. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004619.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28828761 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Guided tissue regeneration for periodontal infra-bony defects.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Apr 19;(2):CD001724. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001724.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 May 29;5:CD001724. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001724.pub3. PMID: 16625546 Updated.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
