Gray Hair: From Preventive to Treatment
- PMID: 40546989
- PMCID: PMC12182098
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S526263
Gray Hair: From Preventive to Treatment
Abstract
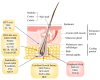
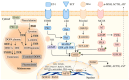
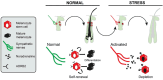
Aging is an inevitable natural process, with gray hair being one of its most visible signs. Hair graying holds psychosocial importance and is an excellent model for studying human pigmentation and aging in an accessible mini-organ. This phenomenon results from decreased melanin production in hair follicles, influenced by genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Gray hair often poses aesthetic concerns and can be accelerated by environmental stressors, lifestyle choices, and nutritional deficiencies. Given the variation in onset and prevalence of gray hair, this study explores the underlying biological factors-namely, genetics, oxidative stress, and hormonal changes-to inform better prevention and treatment strategies. Recent advancements in prevention and treatment, such as topical melanin stimulants, antioxidants, dietary supplements, and low-level laser therapy (LLLT), offer promising approaches to managing gray hair. Understanding gray hair comprehensively-encompassing biological, psychological, and social dimensions-provides valuable insights into the aging process and can enhance overall well-being while addressing the stigma associated with aging. Our comprehensive analysis reveals that while graying correlates with certain health conditions, its primary significance is physiological rather than pathological. This understanding is essential for healthcare providers and the public to approach graying with scientific objectivity rather than social prejudice.
Keywords: aesthetic; aging; curative; hair graying; oxidative stress; preventive.
© 2025 Herdiana.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Surveillance for Violent Deaths - National Violent Death Reporting System, 50 States, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico, 2022.MMWR Surveill Summ. 2025 Jun 12;74(5):1-42. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss7405a1. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2025. PMID: 40493548 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
References
-
- Kojima T, Yamada H, Enomoto S, Nakao T, Arai S. Melanin granules morphology and distribution in human black hair investigated by focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy: differences between Asian and Caucasian hair. J Struct Biol. 2024;216(2):108088. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2024.108088 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Han SY, Kang EK, Choi IS. Iron gall ink revisited: a surfactant-free emulsion technology for black hair-dyeing formulation. Cosmetics. 2021;8(1):1–9. doi: 10.3390/cosmetics8010009 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

