Correlation of intravitreal IL-6 with the formation of epiretinal membrane after successful retinal detachment repair
- PMID: 40546993
- PMCID: PMC12182604
- DOI: 10.1177/25158414251350072
Correlation of intravitreal IL-6 with the formation of epiretinal membrane after successful retinal detachment repair
Abstract
Introduction: Epiretinal membrane (ERM) formation following a successful rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD) operation has been reported to occur in about 4%-15% of the cases. In this study, we collected vitreous samples from patients with RRD to identify whether the concentration of IL-6 is correlated with the presence of postoperative ERM. We aim is to identify whether the inflammatory cascade could be a potential key factor in the ERM pathogenesis.
Methods: This was a prospective single-centre study where 42 eyes were enrolled. All patients underwent 25G PPV. The vitreous sample was collected before the infusion line was opened so that the sample would not be diluted. Then, the sample was centrifuged at 5000 g for 15 min at 15°C. Afterwards, the supernatant fluid was transferred to an Eppendorf tube and stored at -40°C. Electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (ECLIA) was employed for the measurement of IL-6 concentration (pg/ml). All patients had optical coherence tomography (OCT) scans at the macula at 4 weeks, 3 months and 1 year after primary RRD repair to identify the presence of the ERM.
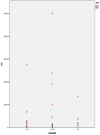
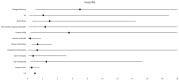
Results: All patients had a follow-up of at least 12 months. The mean BCVA of all 42 eyes at the end of follow-up period was 0.24 ± 0.31 LogMar. The presence of ERM was identified in 28.6% (n = 12) of the patients, and the mean IL-6 concentration was 573.96 ± 1179.58 pg/ml. It appears that the patients who developed a post op ERM had an IL-6 mean concentration value of 173.96 ± 191.25 pg/ml, and the patients with no post op ERM had 733.97 ± 1364.04 pg/ml with p-value = 0.04 < 0.05. Nevertheless, following a multivariate binary logistic regression model, the above results did not appear to be statistically significant.
Conclusion: High concentration of IL-6 in the vitreous of eyes with RRD does not hold a significant role in the ERM pathogenesis. Our study identified the presence of a draining retinotomy as the most significant risk factor for ERM formation following a successful surgical RRD repair.
Keywords: Pars Plana vitrectomy; cytokines; epiretinal membrane; interleukin-6; rhegmatogenous retinal detachment.
© The Author(s), 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous