Evaluation of tumor budding, desmoplastic reaction, and lymphocytic infiltration in predicting survival for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 40547151
- PMCID: PMC12179880
- DOI: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i6.107021
Evaluation of tumor budding, desmoplastic reaction, and lymphocytic infiltration in predicting survival for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Although previous findings indicated that pathological assessment of tumor budding (TB), desmoplastic reaction (DR), and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) may play a role in determining tumor behavior in many malignancies, the relationship between TB, DR, and TILs in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is still unknown.
Aim: To evaluate relationships of TB, DR, and TILs with histopathological parameters and determine their prognostic value in patients with PDAC.
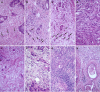
Methods: The study cohort comprised 100 patients diagnosed with PDAC. Peritumoral budding (PTB) and intratumoral budding (ITB) were assessed according to the International Tumor Budding Consensus Conference guidelines. DR was classified based on stromal maturation. TILs were evaluated semiquantitatively with a 5% cutoff. Additionally, cases were categorized into two groups according to lymphocyte density: No/Low lymphocytes and medium/high lymphocytes.
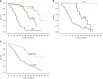
Results: A significant correlation was observed between ITB and PTB (r = 0.890). Higher PTB was associated with fewer TILs and immature stroma (P < 0.001). PTB and TILs were significantly related to tumor dimension, lymphovascular invasion, lymph node metastasis (LNM), and stage (P < 0.005). ITB was also associated with the presence of lymph node involvement. The results of the univariate analysis revealed a significant correlation between poor survival rates and the presence of lymphovascular invasion, LNM, PTB, ITB, and TILs according to scoring (P < 0.001). The multivariate analysis revealed LNM, PTB, ITB, and TILs according to scoring as independent prognostic factors.
Conclusion: TB assessment stratified patients with PDAC. PTB-ITB correlation showed diagnostic relevance of ITB in biopsy specimens. The prognostic significance of DR and interplay with TIL subsets warrant further investigation.
Keywords: Desmoplastic reaction; Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; Prognostic factors; Tumor budding; Tumor microenvironment; Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig AB, Fleshman JM, Matrisian LM. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014;74:2913–2921. - PubMed
-
- Bahra M, Pratschke J, Klein F, Neuhaus P, Boas-Knoop S, Puhl G, Denecke T, Pullankavumkal JR, Sinn M, Riess H, Pelzer U. Cytoreductive Surgery for Pancreatic Cancer Improves Overall Outcome of Gemcitabine-Based Chemotherapy. Pancreas. 2015;44:930–936. - PubMed
-
- Strobel O, Neoptolemos J, Jäger D, Büchler MW. Optimizing the outcomes of pancreatic cancer surgery. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2019;16:11–26. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

