Analysis of serum S100A12, soluble advanced glycation end products receptor, and gut microbiome in elderly patients with colorectal cancer
- PMID: 40547164
- PMCID: PMC12179942
- DOI: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i6.106393
Analysis of serum S100A12, soluble advanced glycation end products receptor, and gut microbiome in elderly patients with colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) ranks among the most prevalent malignancies in elderly populations, and chemotherapy resistance remains a critical clinical challenge. Emerging evidence highlights the interplay between chronic inflammation, gut microbiome dysbiosis, and CRC progression. Proinflammatory cytokines [e.g., interleukin (IL)-6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α)] and mediators like S100 calcium-binding protein A12 (S100A12)/soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products (sRAGE) are implicated in tumorigenesis, while gut microbial imbalances may exacerbate inflammatory microenvironments conducive to chemotherapy resistance. However, the triad relationship between S100A12/sRAGE, gut microbiota profiles, and chemotherapy efficacy in elderly patients with CRC remains unexplored, limiting biomarker-driven therapeutic strategies.
Aim: To analyze the correlation between serum levels of S100A12, sRAGE, gut microbiome dysbiosis, and systemic inflammation in elderly patients with CRC and to assess their predictive value for chemotherapy efficacy.
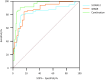
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on the clinical data of 120 elderly patients with advanced-stage CRC who visited our hospital from August 2023 to May 2024. These patients were enrolled in the study group. Additionally, 120 healthy individuals undergoing routine health check-ups during the same period were selected as the control group. Serum S100A12, sRAGE, IL-6, and TNF-α levels were measured by ELISA, and fresh stool samples were collected before chemotherapy to analyze gut microbiome composition in the study group. Follow-up observations were conducted after chemotherapy. Pearson correlation analysis was used to explore the relationship between serum S100A12, sRAGE levels, and gut microbiome dysbiosis in patients with CRC. The predictive diagnostic value of pre-chemotherapy serum S100A12 and sRAGE levels for chemotherapy efficacy was assessed using receiver operating characteristic curves.
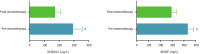
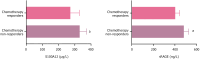
Results: Pre-chemotherapy serum S100A12, sRAGE, IL-6, and TNF-α levels were significantly elevated in patients with CRC vs controls (all P < 0.05). These biomarkers progressively increased with microbiota dysbiosis severity (severe vs mild dysbiosis: S100A12: 340.26 ± 52.39 μg/L vs 302.53 ± 56.97 μg/L; sRAGE: 525.64 ± 37.32 ng/L vs 441.38 ± 48.73 ng/L, P < 0.05) and correlated strongly with IL-6 (r = 0.712) and TNF-α (r = 0.698). Post-chemotherapy, biomarker levels decreased (P < 0.05), coinciding with beneficial microbiota recovery (Bifidobacterium 176%, Lactobacillus 153%) and pathogenic taxa reduction (Escherichia coli 62%). The combined S100A12/sRAGE model predicted chemotherapy resistance with an area under the curve of 0.914 (sensitivity = 86.07%, specificity = 88.89%), outperforming individual biomarkers.
Conclusion: Elevated serum S100A12 and sRAGE in elderly patients with CRC reflected gut microbiome dysbiosis and systemic inflammation, driven by IL-6/TNF-α signaling. Their post-chemotherapy decline parallels microbiota restoration, supporting a microbiome-inflammation-biomarker axis. The combined biomarker model offers robust clinical utility for chemotherapy efficacy prediction and personalized therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Chemotherapy efficacy; Colorectal cancer; Correlation; Elderly; Gut microbiome dysbiosis; Predictive value; Serum S100 calcium-binding protein A12; Soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
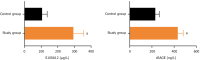
Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Gut microbiota dysbiosis characterized by abnormal elevation of Lactobacillus in patients with immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Aug 25;13:1243512. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1243512. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37692165 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between serum advanced glycation end-products and their receptor-mediated oxidative stress and perinatal outcomes in gestational diabetes mellitus.World J Diabetes. 2025 Jun 15;16(6):104177. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.104177. World J Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 40548277 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble Forms and Ligands of the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End-Products in Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: An Observational Prospective Study.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 14;10(8):e0135857. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135857. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26274928 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li N, Zhou YY, Lu M, Zhang YH, Lu B, Luo CY, Luo JH, Cai J, Chen HD, Dai M. [Participation rate and detection of colorectal neoplasms based on multi-round fecal immunochemical testing for CRC screening in the Chinese population] Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2023;45:1041–1050. - PubMed
-
- Zhao X, Dou LZ, Zhang YM, Liu Y, He S, Ke Y, Liu XD, Liu YM, Wu HR, Li ZQ, Chen ZH, Wang GQ. [Risk factors for residual cancer or lymph node metastasis after endoscopic noncurable resection of early colorectal cancer] Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2023;45:335–339. - PubMed
-
- Bobek D, Sestan M, Mijacika L, Kovacic N, Lukic IK, Grcevic D, Jelusic M. Serum S100A12 levels in children with childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic juvenile arthritis, and systemic undefined recurrent fevers. Z Rheumatol. 2023;82:74–79. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

