Regulator of chromosome condensation 1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation via cell-division-cycle-associated-8 dependent phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B signaling
- PMID: 40547181
- PMCID: PMC12179933
- DOI: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i6.106080
Regulator of chromosome condensation 1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation via cell-division-cycle-associated-8 dependent phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B signaling
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) ranks among the most prevalent and deadly malignancies, characterized by a high recurrence rate. Regulator of chromosome condensation 1 (RCC1) serves as a principal guanine nucleotide exchange factor for ras-related nuclear protein guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) and is implicated in various cancers. However, the role of RCC1 in HCC remains unexplored.
Aim: To elucidate the functional significance and molecular mechanisms of RCC1 in HCC.
Methods: Bioinformatics were to examine the expression levels of RCC1 in HCC and to assess its impact on the prognosis of this malignancy. The cell counting kit-8 assay and flow cytometry were utilized to evaluate the cell viability and cell cycle of HCC cells. Furthermore, quantitative reverse transcription and immunoblotting were to investigate the influence of RCC1 on cyclin associated proteins.
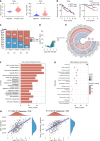
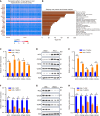
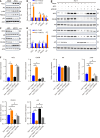
Results: Bioinformatics analysis revealed that RCC1 was highly expressed in HCC and correlated with poor prognosis in HCC patients. Functional studies showed that RCC1 overexpression promoted the malignant phenotype of HCC cells, especially the proliferation of HCC cells, whereas RCC1 knockdown had the opposite effect. Mechanistically, we identified cell division cycle-associated (CDCA) 8 as a downstream target of RCC1 in HCC. RCC1 overexpression markedly increased CDCA8 levels, consequently enhancing cell proliferation and survival in HCC cells. Additionally, we discovered that RCC1 contributed to the development and progression of HCC by activating the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B/cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1a pathway through CDCA8.
Conclusion: Our study provides profound insights into the pivotal role of RCC1 in HCC and its potential as a therapeutic target.
Keywords: Cell cycle; Cell division cycle-associated 8; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway; Proliferation; Regulator of chromosome condensation 1.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
CEP55: Implications for Immunotherapy and Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025;28(8):1345-1362. doi: 10.2174/0113862073298525240522104104. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025. PMID: 38847172
-
STOX1 Isoform A Promotes Proliferation and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Dual Mechanisms of Transcriptionally Upregulation of Cyclin B1 and Activation of ROS-Dependent PTEN/AKT1 Signaling.Cancer Med. 2025 Jul;14(13):e70958. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70958. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 40567110 Free PMC article.
-
Spliced exon9 ADRM1 promotes liver oncogenicity via selective degradation of tumor suppressor FBXW7.J Hepatol. 2025 Jul;83(1):92-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.12.037. Epub 2025 Jan 7. J Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 39788431
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
Ablative and non-surgical therapies for early and very early hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2023 Dec;27(29):1-172. doi: 10.3310/GK5221. Health Technol Assess. 2023. PMID: 38149643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:229–263. - PubMed
-
- Vogel A, Martinelli E ESMO Guidelines Committee. Electronic address: clinicalguidelines@esmo.org; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Updated treatment recommendations for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) from the ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines. Ann Oncol. 2021;32:801–805. - PubMed
-
- Vogel A, Meyer T, Sapisochin G, Salem R, Saborowski A. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2022;400:1345–1362. - PubMed
-
- Huang T, Yang Y, Song X, Wan X, Wu B, Sastry N, Horbinski CM, Zeng C, Tiek D, Goenka A, Liu F, Brennan CW, Kessler JA, Stupp R, Nakano I, Sulman EP, Nishikawa R, James CD, Zhang W, Xu W, Hu B, Cheng SY. PRMT6 methylation of RCC1 regulates mitosis, tumorigenicity, and radiation response of glioblastoma stem cells. Mol Cell. 2021;81:1276–1291.e9. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

