Increased prevalence of parvovirus B19 infection among pregnant women in central Italy and genomic analysis
- PMID: 40547341
- PMCID: PMC12178912
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xagr.2025.100514
Increased prevalence of parvovirus B19 infection among pregnant women in central Italy and genomic analysis
Abstract
Background: During 2024, the number of pregnant women who tested positive for parvovirus B19 in central Italy significantly increased. Genome sequence analysis of parvovirus B19 detected in blood samples of pregnant women revealed the co-circulation of 2 distinct clusters belonging to genotype 1, with nucleotide differences in both nonstructural and VP1 and VP2 proteins. The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control declares a considerable increase in parvovirus B19 infections among children, pregnant women, and blood donors across most European nations from late 2023.
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the positivity rate of parvovirus B19 infections among Italian pregnant women attending the maternal-fetal infection prevention outpatient care facility at the National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani of Rome for routine evaluation of maternal-fetal infections.
Study design: Blood samples from 139 pregnant women were analyzed for parvovirus B19 infection according to the physician's request: parvovirus B19 immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin G antibodies and/or parvovirus B19 DNA. Among these samples, 8 positive for parvovirus B19 DNA were subjected to target amplicon sequencing and whole-genome reconstruction. For phylogenetic analysis, all parvovirus B19 complete genome sequences were collected, and multisequence alignment was performed to develop the best tree model.
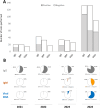
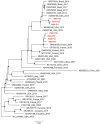
Results: A sharp increase in parvovirus B19 circulation among Italian pregnant women occurred, starting from the end of 2023. During the first 9 months of 2024, requests for diagnosis of parvovirus B19 infection continued to increase significantly, and 46% of the samples analyzed in the first 9 months of the year were positive for parvovirus B19 infection. Phylogenetic analysis showed that all viruses detected belonged to parvovirus B19 genotype 1 and were clustered in 2 separate phylogenetic groups: one similar to the PP818758 genome sequence from France in 2024 and one similar to the KM393165 genome sequence from the United States in 2013. In addition, whole-genome sequence alignment revealed nucleotide mutations that caused amino acid changes, distinguishing the National Institute for Infectious Diseases clusters from similar sequences: the F8L, R54K, and F517S substitutions in the nonstructural gene of the viral genome for cluster 1 and the C298S, E195D, and T456S mutations in the nonstructural, VP1, and VP1 + VP2 genes for cluster 2. Furthermore, the C298S mutation was observed for the first time, as this mutation has never been detected in any other parvovirus B19 genome sequences submitted to international databases.
Conclusion: Since the beginning of 2024, Italy, similar to many European countries, has been experiencing an epidemic of parvovirus B19 infection among pregnant women, with a positivity rate increasing to 46% in the first 9 months of the year. The peak incidence observed in this period seems to be significantly higher than that observed in the same period of the years 2021-2023. Because parvovirus B19 infection can cause up to 20% of asymptomatic infections with serious consequences for the fetus, it is essential to enhance screening and surveillance to stop virus transmission and dissemination, particularly during epidemic periods.
Keywords: Italy; parvovirus B19; parvovirus B19 genotype; phylogenetic analysis; pregnant women.
© 2025 The Authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 06;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. PMID: 17253490 Updated.
-
Behavioral interventions to reduce risk for sexual transmission of HIV among men who have sex with men.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD001230. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001230.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. PMID: 18646068
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic mastectomy for the prevention of breast cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004 Oct 18;(4):CD002748. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002748.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Nov 10;(11):CD002748. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002748.pub3. PMID: 15495033 Updated.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
References
-
- Communicable disease threats report. week 16. European Center for Disease Prevention and Control. 2024. Available at:https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/communicable-disease-thr.... Accessed XXX.
-
- Guillet M., Bas A., Lacoste M., et al. New atypical epidemiological profile of parvovirus B19 revealed by molecular screening of blood donations, France, winter 2023/24/24. Euro Surveill. 2024;29:1560–7917. ES.2024.29.21.2400253. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

