Cell macroencapsulation devices in contemporary research: A systematic review
- PMID: 40547419
- PMCID: PMC12180967
- DOI: 10.1016/j.reth.2025.05.013
Cell macroencapsulation devices in contemporary research: A systematic review
Abstract
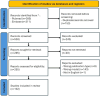
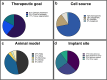
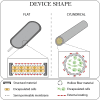
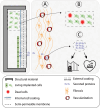
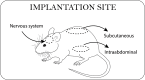
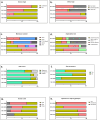
Cell macroencapsulation devices (CMDs) represent a promising therapeutic approach by combining controlled, off-the-shelf technology with living tissue functionality. Despite their potential, the current knowledge about CMD development and implementation remains fragmented across different applications. We conducted a systematic review to synthesize the available evidence on implantable CMDs and establish a comprehensive framework for their development. Our analysis cataloged studies based on device materials and design, cell types, implantation strategies, and evaluation methods. The review revealed that CMD development has largely progressed in application-specific silos, with varying approaches to device characterization, cell selection (from xenogeneic to autologous), and assessment methods. Key evaluation parameters included cell survival and functionality, host tissue response (inflammation, vascularization, and fibrosis), and therapeutic efficacy. While successful implementations exist across multiple applications, the lack of standardized development and evaluation protocols emerges as a significant barrier to cross-application advancement. These findings highlight the need for unified assessment frameworks to accelerate CMD development across therapeutic applications.
Keywords: Bioencapsulation; Biomedical devices; Cell encapsulation; Implantation; Therapeutic delivery.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Eliciting adverse effects data from participants in clinical trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 16;1(1):MR000039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000039.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29372930 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the effectiveness of inhaler devices in asthma and chronic obstructive airways disease: a systematic review of the literature.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(26):1-149. doi: 10.3310/hta5260. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701099
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Structured treatment interruptions (STI) in chronic unsuppressed HIV infection in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Jul 19;2006(3):CD006148. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006148. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. PMID: 16856117 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise interventions and patient beliefs for people with hip, knee or hip and knee osteoarthritis: a mixed methods review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 17;4(4):CD010842. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010842.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29664187 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

