Effects of boxing interventions on physical fitness and health-related quality of life in older people with Parkinson's disease: a systematic review with meta-analysis
- PMID: 40547458
- PMCID: PMC12179875
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1589512
Effects of boxing interventions on physical fitness and health-related quality of life in older people with Parkinson's disease: a systematic review with meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: This systematic review with meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the available body of published peer-reviewed studies on the effects of boxing (BOX) interventions on balance, cardiorespiratory fitness, motor function, and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in older people with Parkinson's disease (PD).
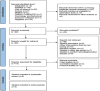
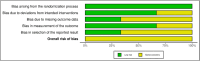
Methods: A comprehensive search of the literature, including peer-reviewed randomized and non-randomized controlled trials, was conducted to December 2024 in the databases of PubMed, Medline, Psychology and Behavioral Sciences Collection (EBSCO), CINAHL Complete, Scopus, and Web of Science (core collection). A random-effects model was employed, and Hedge's g effect sizes (ES) were computed. The GRADE, RoB 2, ROBIN-1, TESTEX, and PRISMA tools evaluated the methodological quality and certainty of evidence. The protocol (code: CRD42024614097) was registered in PROSPERO.
Results: Eight studies were included, with 100 older people with PD, of which only three could be meta-analyzed. No significant effects were evident (p = 0.05), which were small to moderate effects of BOX on ABC-Scale (ES = -0.56; p = 0.13), Timed Up-And-Go (TUG; ES = 0.24; p = 0.34), TUG dual task (ES = 0.20; p = 0.41), 6-min walking test (ES = 2.16; p = 0.23), and PD Quality of Life Questionnaire (ES = -0.009; p = 0.98).
Conclusion: BOX interventions do not significantly improve balance, cardiorespiratory fitness, and health-related quality of life in older people with PD.
Keywords: aged; dopamine; neurodegenerative diseases; physical functional performance; postural balance.
Copyright © 2025 Hernandez-Martinez, Cid-Calfucura, Vázquez-Carrasco, Fritz-Silva, Herrera-Valenzuela, Branco, Zapata-Bastias and Valdés-Badilla.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

