Evaluating ECAMM-based training efficacy for malaria microscopists in Hunan Province, China
- PMID: 40547467
- PMCID: PMC12179097
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1598917
Evaluating ECAMM-based training efficacy for malaria microscopists in Hunan Province, China
Abstract
Background: The rapid and accurate diagnosis of malaria has contributed to China's remarkable achievement in malaria elimination. In the post-elimination phase, microscopic examination remains crucial for preventing the reintroduction of imported malaria. This study developed and validated a 4-day external competency assessment training program for malaria microscopists based on the External Competency Assessment for Malaria Microscopists (ECAMM) framework, to enhance diagnostic proficiency among laboratory personnel in public health institutions.
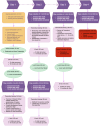
Methods: Course design, blood smear selection, evaluation methods, and scoring criteria strictly adhered to WHO guidelines. Participants underwent one pre-training test and four post-training assessments involving 48 blood smears to evaluate diagnostic accuracy in qualitative identification and species differentiation. A comprehensive analysis was conducted on training needs, skill improvement trajectories, diagnostic error patterns, competency predictors, and participant satisfaction. 24 participants from public health institutions across 14 prefecture-level jurisdictions in Hunan Province completed the program with heterogeneous performance outcomes.
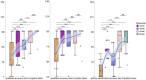
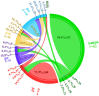
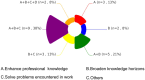
Results: 75% of participants had received no formal malaria microscopy training in the preceding 5 years. Post-training assessments demonstrated significant improvements: negative smear recognition accuracy increased by 29.86%, positive smear identification by 25.52%, and species differentiation accuracy by 48.96%. The predominant diagnostic error was interspecies confusion, notably the misidentification of Plasmodium ovale (P. ovale) as Plasmodium malariae (P. malariae)(20.8% of errors). Trainee competency showed no significant correlation with age, gender, or educational background (p > 0.05). Participant satisfaction ratings consistently reached "very satisfied" with almost all training components.
Conclusion: This external capacity assessment training program effectively enhanced short-term malaria microscopy proficiency. We propose institutionalizing this model as a national certification program to maintain diagnostic competency through regular training and quality monitoring, particularly targeting primary healthcare facilities at the township level.
Keywords: ECAMM; competency; malaria; microscopist; training course.
Copyright © 2025 Ning, Zhuang, Wen, Xu, Wang, Peng, Huang and Tian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . World malaria report 2023. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2023).
-
- World Health Organization . World malaria report 2024: Addressing inequity in the global malaria response. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2024).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

