A comprehensive mechanism of biological and health effects of anthropogenic extremely low frequency and wireless communication electromagnetic fields
- PMID: 40547468
- PMCID: PMC12179773
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1585441
A comprehensive mechanism of biological and health effects of anthropogenic extremely low frequency and wireless communication electromagnetic fields
Abstract
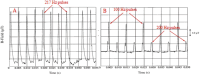
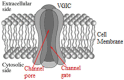
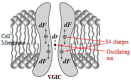
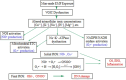
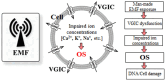
Exposure to anthropogenic electromagnetic fields (EMFs), especially those of wireless communications (WC) has increased tremendously. This is an unprecedented phenomenon throughout biological evolution because, all anthropogenic EMFs, being fully polarized, coherent, and, especially WC EMFs, highly variable, differ substantially from the natural EMFs. WC EMFs consist of Microwave (MW) carrier waves, modulated, by Extremely Low Frequency (ELF) signals, and included in on/off pulses repeated at various ELF rates. Moreover, they exhibit intense random variability, mainly in the Ultra Low Frequency (ULF) band. Thus, WC EMFs are a combination of MW and ELF/ULF EMFs. The combination of polarization/coherence and intense low-frequency (ELF/ULF) variability seems to be the key to EMF-bioactivity. Epidemiological and laboratory studies highlight a connection between ELF or WC EMF exposure and cancer, infertility, electro-hypersensitivity, and various other pathologies. Studies also find DNA damage and Oxidative Stress (OS) which explain these pathologies. While man-made EMFs cannot directly ionize molecules, they are capable of doing this indirectly in biological tissue, by triggering the biosynthesis of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) which can damage biomolecules, including DNA. The (over)production of ROS and the consequent OS are triggered by irregular gating of Voltage-Gated Ion Channels (VGICs) in the cell membranes as described by the Ion Forced Oscillation (IFO)-VGIC mechanism: Mobile ions within VGICs forced to oscillate by the applied ELF/ULF EMFs exert forces on the voltage sensors of the VGICs, similar to or greater than the forces that physiologically gate those channels, resulting in their irregular gating (dysfunction). Dysfunction of ion channels disrupts intracellular ionic concentrations. This triggers ROS overproduction and OS by the ROS-generating systems/enzymes in the cells, such as the electron transport chain (ETC) in the mitochondria, or the NADPH/NADH oxidases (NOXs), the Nitric Oxide synthases (NOS), etc. The IFO-VGIC mechanism and the consequent OS constitute a comprehensive mechanism that explains all known adverse biological and health effects reported to be induced by anthropogenic EMFs.
Keywords: DNA damage; IFO-VGIC mechanism; ROS; electromagnetic fields; ion forced oscillation; oxidative stress; voltage-gated ion channels.
Copyright © 2025 Panagopoulos, Yakymenko, De Iuliis and Chrousos.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exploring the influence of Schumann resonance and electromagnetic fields on bioelectricity and human health.Electromagn Biol Med. 2025;44(3):348-358. doi: 10.1080/15368378.2025.2508466. Epub 2025 May 20. Electromagn Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 40394813 Review.
-
Human‑made electromagnetic fields: Ion forced‑oscillation and voltage‑gated ion channel dysfunction, oxidative stress and DNA damage (Review).Int J Oncol. 2021 Nov;59(5):92. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5272. Epub 2021 Oct 7. Int J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34617575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Misek J, Jakus J, Hamza Sladicekova K, Zastko L, Veternik M, Jakusova V, et al. Extremely low frequency magnetic fields emitted by cell phones. Front Phys. (2023) 11:1094921. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2023.1094921 - DOI
-
- Panagopoulos DJ, Karabarbounis A, Lioliousis C. Defining wireless communication (WC) electromagnetic fields (EMFs): A. Polarization is a principal property of all man-made EMFs; B. Modulation, pulsation, and variability are inherent parameters of WC EMFs; C. Most man-made EMF exposures are non-thermal; D. Measuring incident EMFs is more relevant than specific absorption rate (SAR); E. All man-made EMFs emit continuous waves, not photons; F. Differences from natural EMFs. Interaction with matter In: Panagopoulos DJ, editor. Electromagnetic fields of wireless communications: Biological and health effects. Boca Raton: CRC Press; (2022)
-
- Pedersen GF. Amplitude modulated RF fields stemming from a GSM/DCS-1800 phone. Wirel Netw. (1997) 3:489–98. doi: 10.1023/A:1019158712657 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

