Non-invasive biomarkers for brain aging: the role of autophagy-related microRNAs in plasma exosomes
- PMID: 40547480
- PMCID: PMC12179099
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2025.1588007
Non-invasive biomarkers for brain aging: the role of autophagy-related microRNAs in plasma exosomes
Abstract
Aim: This study aimed to identify autophagy-related microRNAs (miRNAs) in plasma exosomes as non-invasive biomarkers for brain aging and explore their potential to improve early detection of age-associated neurodegeneration. With the increasing incidence of neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), frontotemporal dementia (FTD), and Parkinson's disease (PD), non-invasive diagnostic tools are urgently needed.
Methods: Plasma samples were collected from 200 individuals, divided into three groups, including young (20-40 years), middle-aged (41-60 years), and elderly (> 60 years). Exosomes were isolated, followed by small RNA sequencing (sRNA-seq) to identify differentially expressed miRNAs, and differentially expressed miRNAs related to autophagy were validated using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Spearman correlation analysis was performed to assess the relationship between autophagy-related miRNAs and brain aging biomarkers. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was conducted to evaluate the diagnostic performance.
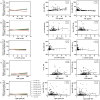
Results: Nine autophagy-related miRNAs were identified and validated as significantly upregulated in plasma exosomal from elderly, including hsa-miR-2110, hsa-miR-18a-3p, hsa-miR-766-3p, hsa-miR-4446-3p, hsa-miR-4667-5p, hsa-miR-4433b-3p, hsa-miR-146a-5p, hsa-miR-423-5p, and novel_260. These miRNAs were validated by qRT-PCR. Correlation analysis showed that several of these miRNAs, such as hsa-miR-2110 and hsa-miR-766-3p, were strongly correlated with NfL (r = 0.68, p = 0.002), Aβ42 (r = 0.62, p = 0.004), and p-Tau181 (r = 0.55, p = 0.008). ROC curve analysis showed that combining these miRNAs with NfL resulted in an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.92, outperforming NfL alone (AUC = 0.85) and miRNAs alone (AUC = 0.84). Further subgroup analysis revealed that multiple miRNAs, such as miR-2110, miR-4446-3p, and novel_260, achieved high AUCs (>0.83) in distinguishing middle-aged adults (41-60 years) from older adults (>60 years), supporting their potential utility for early detection of age-associated neurodegeneration.
Conclusion: This study identifies a set of autophagy-related miRNAs as promising biomarkers for brain aging. The combination of these miRNAs with traditional biomarkers offers a non-invasive and highly sensitive method for early detection of brain aging, providing significant potential to enhance diagnostic accuracy in neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: autophagy; biomarkers; brain aging; exosomes; miRNA.
Copyright © 2025 Cheng, Yu, Cui, Chen, Fan, Yu, Jin, Wang, Li and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Brickman A. M., Manly J. J., Honig L. S., Sanchez D., Reyes-Dumeyer D., Lantigua R. A., et al. (2021). Plasma p-tau181, p-tau217, and other blood-based Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers in a multi-ethnic, community study. Alzheimers Dement. 17, 1353–1364. doi: 10.1002/alz.12301, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

