Zinc sulfate improves insulin resistance, oxidative stress and apoptosis in liver tissues of PCOS rats through the NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 40547527
- PMCID: PMC12178883
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1569866
Zinc sulfate improves insulin resistance, oxidative stress and apoptosis in liver tissues of PCOS rats through the NF-κB pathway
Abstract
Background: Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is primarily characterized by insulin resistance, which leads to increased hepatic glucose production and impaired insulin-mediated glucose disposal. Pathologically, this condition manifests as elevated liver cell apoptosis and reduced lipid transport capacity, further exacerbating insulin resistance. Liver cell apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction are key pathological features of PCOS-associated liver diseases, contributing significantly to the progression of PCOS. Although zinc sulfate is recognized for its antioxidant properties, its efficacy in ameliorating PCOS-related liver damage remains unclear.
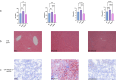
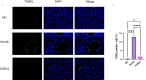
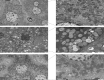
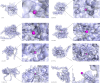
Methods: Female Sprague-Dawley rats were induced with PCOS and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) through a high-fat diet and letrozole administration over 28 days. Subsequently, the model rats received zinc sulfate treatment via gavage once daily for an additional 21 days. Serum hormone levels and biochemical markers were assessed using ELISA and enzymatic assays. Histological examination of ovarian and liver tissues was performed using hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining, while hepatic lipid accumulation was evaluated by Oil Red O staining. Transmission electron microscopy was employed to examine liver cell ultrastructure, and TUNEL staining was used to assess hepatocellular apoptosis. Transcriptome sequencing was conducted on liver tissues to identify key genes and pathways, which were further validated by Western blotting and immunohistochemistry.
Results: Initial blood sampling revealed decreased serum zinc concentration in the PCOS group, alongside elevated levels of testosterone (T), luteinizing hormone (LH), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), blood glucose, fasting insulin, and oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) values. However, the levels of serum estrogen (E2) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) in the PCOS group were significantly decreased. Markers of oxidative stress, including malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione disulfide/glutathione ratio (GSSG/GSH), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX), and catalase (CAT), were also increased. Zinc sulfate treatment effectively improved all these parameters. HE and Oil Red O staining confirmed that zinc sulfate mitigated high-fat diet and letrozole-induced fatty liver. Furthermore, zinc sulfate alleviated severe hepatocellular apoptosis and mitochondrial damage observed in PCOS rats. Transcriptomic analysis indicated that zinc sulfate primarily mitigated PCOS-related liver damage via the cholesterol synthesis pathway, and experimental validation demonstrated that zinc sulfate inhibited oxidative stress and apoptosis in liver cells through the NF-κB pathway.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates that zinc sulfate ameliorates liver oxidative stress and apoptosis in PCOS by modulating the NF-κB pathway, offering a novel therapeutic approach for managing PCOS-associated liver diseases.
Keywords: hepatic lipid deposition; mitochondrial damage; oxidative stress; polycystic ovary syndrome; zinc sulfate.
Copyright © 2025 Kang, Zhao and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Buzhong Yiqi decoction improves inflammation and oxidative damage in autoimmune thyroiditis by inhibiting apoptosis via the SIRT1-Mediated Nrf2/NF-κB axis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;351:119967. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119967. Epub 2025 May 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40360040
-
Study on the modulation of kidney and liver function of rats with diabetic nephropathy by Huidouba through metabolomics.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;351:120136. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120136. Epub 2025 Jun 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40513925
-
Antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects of Carvacrol against polycystic ovary syndrome associated complications using high fat diet and Letrozole challenged rat model: a multidisciplinary study cascading in vivo, in vitro, in silico and network pharmacology approaches.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Aug;33(8):4703-4724. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01809-8. Epub 2025 Jun 20. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40540113
-
Effects of quercetin on polycystic ovary syndrome in animal models: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024 Apr 18;22(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12958-024-01220-y. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 38637876 Free PMC article.
-
Ovarian surgery for symptom relief in women with polycystic ovary syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 10;11(11):CD009526. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009526.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29125183 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

