Identification of a Natural Small Molecule Dauricine for Glioma Therapy through Targeting p53 and VEGFA Pathways
- PMID: 40547611
- PMCID: PMC12177586
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c01334
Identification of a Natural Small Molecule Dauricine for Glioma Therapy through Targeting p53 and VEGFA Pathways
Abstract
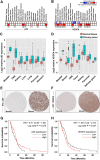
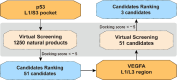
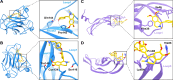
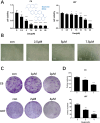
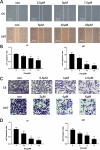
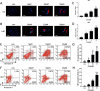
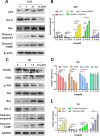
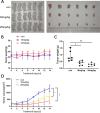
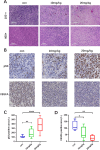
Glioma is a highly malignant primary brain tumor with a poor prognosis. Current treatments for intracranial glioma are often ineffective, necessitating the development of novel therapeutic agents. In this work, molecular docking-based screening analyses were conducted to identify dauricine as a dual-targeted agent of p53 and VEGFA by targeting the Loop1/Sheet3 (L1/S3) pocket of p53 and the Loop1/Loop3 (L1/L3) regions of VEGFA. The anticancer activity of dauricine was further evaluated using MTT, colony formation, wound-healing, transwell invasion, Western blot, and apoptosis assays, including Hoechst staining and flow cytometry on U87 and C6 glioma cell lines. A C6 xenograft model in BALB/c-nu mice was used to assess tumor growth inhibition. The in vivo anticancer effect of dauricine was detected by HE staining, and the levels of p53 and VEGFA were tested by IHC staining. The results showed that dauricine significantly inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion of glioma cells, induced apoptosis, and reduced tumor growth both in vitro and in vivo. Western blot analyses showed that dauricine upregulated p53 and downregulated VEGFA pathways. In vivo experiments demonstrated that dauricine inhibited the growth of subcutaneous tumors in nude mice by targeting p53 and VEGFA. Overall, these results demonstrated that dauricine suppresses glioma growth by targeting the p53 and VEGFA pathways, making it a promising anticancer agent for glioma treatment.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(45):iii-iv, ix-221. doi: 10.3310/hta11450. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999840
-
Diagnostic test accuracy and cost-effectiveness of tests for codeletion of chromosomal arms 1p and 19q in people with glioma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Mar 2;3(3):CD013387. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013387.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35233774 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Molecular feature-based classification of retroperitoneal liposarcoma: a prospective cohort study.Elife. 2025 May 23;14:RP100887. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100887. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40407808 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
