Investigation of the Enhancement Effect of Coloading of Compounds with Different Hydrophobicities on the Stability of a Phospholipid/Bile Salt Mixed Micellar System
- PMID: 40547638
- PMCID: PMC12177587
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c11475
Investigation of the Enhancement Effect of Coloading of Compounds with Different Hydrophobicities on the Stability of a Phospholipid/Bile Salt Mixed Micellar System
Abstract
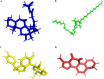
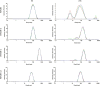
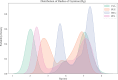
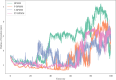
Bile acid salt (BAS) micellar structures containing phospholipids (PPLs) have many important applications in the field of drug delivery on account of their biocompatibility, but improving their structural stability is a crucial issue for further development. Combined with our previous findings, we hypothesized that coloading of drugs with different hydrophobicities can enhance the structural stability of the micelles. Puerarin (PUE) and tanshinone IIA (TSA) from the Chinese couplet medicines, Radix Puerariae-Salvia miltiorrhiza, were chosen as the model hydrophobic compound pair to be encapsulated into mixed micelles composed of BAS and PPL (BPMM), to form four mixed micellar systems, including blank BPMM, single-drug-carrying BPMM (namely, PUE-loaded BPMM (P-BPMM) and TSA-loaded BPMM (T-BPMM)), and coloaded BPMM (PT-BPMM). The hypothesis was confirmed by comparing the stability of blank BPMM with those of drug-loaded BPMM, single-drug-carrying and drug-cocarrying BPMM, by utilizing molecular dynamics (MD) simulations combined with various experimental observations. Moreover, it is found that the drug distribution preference in the system is not significant when a single drug is loaded. However, when coloaded, the distribution preference of different hydrophobic drugs in the same space is reflected, that is, a more appropriate spatial distribution of drugs in the micellar system can effectively improve the drug-loading stability of the system. The strategy to improve the stability of mixed micelles in this investigation avoids the complex processes associated with modifying the structure of micellar carrier materials and offers the advantages of the use of biosurfactants for drug delivery.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Comparison of cellulose, modified cellulose and synthetic membranes in the haemodialysis of patients with end-stage renal disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234.pub2. PMID: 11687058 Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Atypical antipsychotics for disruptive behaviour disorders in children and youths.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Aug 9;8(8):CD008559. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008559.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28791693 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang Z., Zhitomirsky I.. Bile Acid Salt as a Vehicle for Solubilization and Electrodeposition of Drugs and Functional Biomolecules for Surface Modification of Materials. Biomedical Materials & Devices. 2024;2(1):397–406. doi: 10.1007/s44174-023-00092-x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
