Ultra-sensitive Quantification of Mid-regional Proadrenomedullin in Human Plasma Using Micro-liquid Chromatography Coupled to Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 40547652
- PMCID: PMC12177583
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c11248
Ultra-sensitive Quantification of Mid-regional Proadrenomedullin in Human Plasma Using Micro-liquid Chromatography Coupled to Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
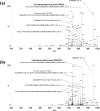
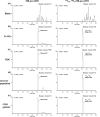
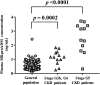
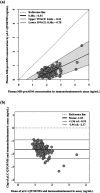
Mid-regional proadrenomedullin (MR-proADM) has been suggested to be a powerful biomarker for the onset, progression, and mortality of various diseases. To achieve sensitive quantification of MR-proADM without cross-reactivity, we established micro-liquid chromatography coupled to the quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (μLC-QTOF/MS) method using IonKey technology. 100 μL of plasma sample was pretreated by protein precipitation followed by solid-phase extraction. Using the established μLC-QTOF/MS method, plasma MR-proADM concentrations were measured in 198 individuals of the Japanese general population, 13 patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) stage G3b-G4 (nondialysis), and 12 patients with CKD stage G5 (dialysis). The novel assay fulfilled the requirements of the US Food and Drug Administration guidance for bioanalytical method validation, with a lower limit of quantification of 0.05 ng/mL. Recovery rates from human plasma and matrix effects were 89.6-114.2% and 95.3-111.7%, respectively. Median plasma MR-proADM concentrations were 0.48, 1.16, and 2.75 ng/mL in general population, CKD stage G3b-G4, and CKD stage G5, respectively (p < 0.0001). All measured concentrations were within the calibration range (0.05-100 ng/mL). The robust Passing-Bablok regression plot between MR-proADM concentrations measured by μLC-QTOF/MS and by immunoluminometric assay showed systemic and proportional bias between methods. The values measured by the μLC-QTOF/MS method tended to be lower than those by immunoluminometric assay. An ultrasensitive and selective method using μLC-QTOF/MS for measuring plasma MR-proADM was established. The novel method can be used in the general population and patients and may have better specificity for MR-proADM than the immunoluminometric assay; thus, it may improve the performance of MR-proADM as a biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with various diseases.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
