Evaluation of the impact of a family physician-led lifestyle clinic on overweight and obesity: A clustered randomized trial in Hail, Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 40547737
- PMCID: PMC12178518
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1969_24
Evaluation of the impact of a family physician-led lifestyle clinic on overweight and obesity: A clustered randomized trial in Hail, Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Objective: This trial evaluated the effectiveness of a joint health coach and dietitian lifestyle clinic led by a family physician for overweight and obese adults in lowering body mass index (BMI) and improving waist circumference (WC) measurement among overweight and obese individuals.
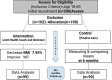
Design and setting: The study was a 6-month, parallel, open-label, clustered, randomized trial with control involving four primary health care centers in Hail City.
Participants: Of the 300 healthy adult volunteers screened, 198 met the inclusion criteria and completed the study. Participants were randomized into four clusters and assigned to either the intervention or control group.
Intervention: A structured dietary, physical exercise, behavioral, and cognitive lifestyle intervention provided by a joint health coach and dietitian clinic led by a family physician.
Primary measures: The primary outcomes were reductions in BMI, improvements in WC distribution, and weight loss differences from baseline to 6 months, with a target of 5% weight loss.
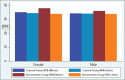
Results: A significant reduction in BMI in the intervention arm (mean BMI intervention before = 36.74, mean BMI intervention after = 33.82, mean difference = 2.91, P < 0.001) compared to the control (routine care) arm is evident. Additionally, the intervention group had notable improvements in WC measurements; however, it is not statistically significant.
Conclusion: The joint lifestyle clinic run by a health coach and a dietitian and led by a family physician is effective in reducing BMI and improving WC measurement. The trial was registered with ClinicalTrials.gov under the identification number NCT05654337 and did not receive specific funding.
Keywords: Body mass index; cluster trial; comparative study; intervention program; obesity; waist circumference.
Copyright: © 2025 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ryan D, Barquera S, Barata Cavalcanti O, Ralston J. Handbook of Global Health. Springer; 2021. The global pandemic of overweight and obesity: Addressing a twenty-first century multifactorial disease; pp. 73–739.
-
- Alanazi J, Unnisa A, Patel R, Itumalla R, Alanazi M, Alharby T, et al. Prevalence of cardiovascular disease and osteoarthritis in obese population of Hail region, Saudi Arabia. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022;26:7161–8. - PubMed
-
- Alreshidi F, Alreshidi F, Ahmed H. An insight into the prevalence rates of obesity and its related risk factors among the Saudi community in the Hai'l Region. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022;26:5755–62. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous