Comparison of in vitro (fish cell line) and in vivo (fish and crustacean) acute toxicity tests in aquatic toxicology
- PMID: 40547851
- PMCID: PMC12178631
- DOI: 10.17221/161/2020-VETMED
Comparison of in vitro (fish cell line) and in vivo (fish and crustacean) acute toxicity tests in aquatic toxicology
Abstract
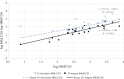
The use of in vitro (fish cell lines) is a cost-effective, very rapid, and informative tool for toxicological assessments. Using the neutral red (NR) assay, we compared the in vitro acute toxicity (20hEC50) of twenty-six chemical substances on a rainbow trout gonad cell line (RTG-2) with their in vivo acute toxicity to Barbados Millions Poecilia reticulata (48hLC50, OECD 203) and crustacean Daphnia magna (48hEC50, OECD 202). The 20hEC50 values obtained by the NR assay were higher in nearly all the cases when compared to the 48hLC50 in P. reticulata and the 48hEC50 in D. magna, indicating that the sensitivity of the RTG-2 cell line was lower compared to P. reticulata and D. magna. A high (r = 0.89) and significant (P < 0.001) correlation was recorded between the 20hEC50 values of the RTG-2 and the 48hEC50 values of D. magna. The correlation between the 20hEC50 values of the RTG-2 and the 48hLC50 values of P. reticulata was lower (r = 0.65; P < 0.001), but also significant. The authors recommend use of the NR assay on the RTG-2 cell lines as a screening protocol to evaluate the toxicity of xenobiotics in aquatic environments to narrow the spectrum of the concentrations for the fish toxicity test.
Keywords: Daphnia magna; NR assay; Poecilia reticulata; cytotoxicity; fish cell line RTG-2.
Copyright: © 2021 Kolarova et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rapid, point-of-care antigen tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 22;7(7):CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35866452 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
The use of irinotecan, oxaliplatin and raltitrexed for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 May;12(15):iii-ix, xi-162. doi: 10.3310/hta12150. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18462574
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
References
-
- Ahne W. Untersuchungen uber die Verwendung von Fischzellkulturen fur Toxizitatsbestimmungen zur Einschrankung und Ersatz des Fischtests [Use of fish cell cultures for toxicity determination in order to reduce and replace the fish tests]. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1985 May;180(5-6):480-504. German. - PubMed
-
- Araujo CS, Marques SA, Carrondo MJ, Goncalves LM. In vitro response of the brown bullhead catfish (BB) and rainbow trout (RTG-2) cell lines to benzo[a]pyrene. Sci Total Environ. 2000 Mar 20;247(2-3):127-35. - PubMed
-
- Babin MM, Canas I, Tarazona JV. An in vitro approach for ecotoxicity testing of toxic and hazardous wastes. Span J Agric Res. 2008 Oct;6(S1):124-8.
-
- Bols NC, Bolinska SA, Dixon DG, Hodson DV, Kaiser KLE. The use of fish cell-cultures as an indication of contaminant toxicity to fish. Aquat Toxicol. 1985 Mar;6(2):147-55.
-
- Borenfreund E, Puerner JA. Toxicity determined in vitro by morphological alternations and neutral red absorption. Toxicol Lett. 1985 Mar;24(2-3):119-24. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
