Screening for Heart Failure in Patients with Hypertension And/Or Diabetes Using Hand-Held Echocardiography: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 40547874
- PMCID: PMC12180437
- DOI: 10.5334/gh.1439
Screening for Heart Failure in Patients with Hypertension And/Or Diabetes Using Hand-Held Echocardiography: A Pilot Study
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to assess the feasibility and cost-effectiveness of hand-held echocardiography-based screening for Stage B or C heart failure among individuals with hypertension and/or diabetes at the High-tech Area Fangcao Community Health Service Center and the Tianfu New Area Huayang Community Health Service Center in Chengdu, China, with the objective of promoting early diagnosis and intensified care.
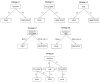
Methods: Patients with hypertension and/or diabetes registered and cared for at two community health service centers (CHSCs; Chengdu, China) with no history of clinical heart failure were recruited between October 2021 and December 2021. By combining symptom assessment (dyspnea and/or edema) and N-terminal-probrain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP ≥ 125 pg/ml as the cut-off) levels with HHE for any indexed abnormality in the dedicated semi-quantitative protocol, patients were categorized into heart failure (HF) Stages A, B, and C. The diagnostic accuracy and cost-effectiveness of several pre-specified screening strategies were compared.
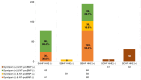
Results: Of the 423 patients (70 ± 9 years; males, 46.6%) enrolled, 166 (39.2%) were symptomatic and 106 (25.1%) exhibited elevated NT-proBNP levels. Hand-held echocardiography (HHE) abnormalities were detected in 286 (67.0%) patients, with interventricular septum thickening (47.0%) being the most common finding, followed by left atrial enlargement (30.0%). Left ventricular systolic dysfunction was identified in 18 (4.3%) patients. A total of 240 (56.7%) patients were reclassified as HF Stage B and 59 (13.9%) as Stage C. The stepwise strategy of using symptoms for initial stratification, followed by the selection of HHE or NT-proBNP in different circumstances, resulted in 100% accuracy and a 31.3% reduction in costs.
Conclusions: HHE-based focused HF screening allows for the early identification of numerous cases of Stage B and mild Stage C HF in high-risk populations. A stepwise screening strategy incorporating symptoms, NT-proBNP, and HHE is feasible and cost-effective and should be adopted in community-based primary care settings.
Keywords: Community health service center; Hand-held echocardiography; Heart failure; Screening.
Copyright: © 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exploring heart failure prevalence and dimensions: A comprehensive NT-proBNP study in high-risk primary care patients.ESC Heart Fail. 2025 Aug;12(4):2834-2842. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.15290. Epub 2025 Jun 2. ESC Heart Fail. 2025. PMID: 40454935 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence-Based Application of Natriuretic Peptides in the Evaluation of Chronic Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction in the Ambulatory Outpatient Setting.Circulation. 2025 Apr 8;151(14):976-989. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.124.072156. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Circulation. 2025. PMID: 39840432
-
Diagnosing Acute Heart Failure in the Emergency Department: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Acad Emerg Med. 2016 Mar;23(3):223-42. doi: 10.1111/acem.12878. Epub 2016 Feb 13. Acad Emerg Med. 2016. PMID: 26910112
-
Brain natriuretic peptide and N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide for the diagnosis of haemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus in preterm neonates.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Dec 8;12(12):CD013129. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013129.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36478359 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis of diagnosis of heart failure, with modelling of implications of different diagnostic strategies in primary care.Health Technol Assess. 2009 Jul;13(32):1-207, iii. doi: 10.3310/hta13320. Health Technol Assess. 2009. PMID: 19586584
References
-
- Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation. 2022;145(18):e895–e1032. DOI: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001063 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

