Efficacy and safety of Eribulin-based chemotherapy in HER2 negative advanced breast cancer patients: a real-world study
- PMID: 40548107
- PMCID: PMC12179173
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1499701
Efficacy and safety of Eribulin-based chemotherapy in HER2 negative advanced breast cancer patients: a real-world study
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is recognized as one of the most common cancers worldwide, exhibiting a notably high incidence rate among women in China. Despite significant advancements in therapeutic approaches, the prognosis for patients diagnosed with advanced stages of the disease remains poor. Therefore, there is an urgent necessity to investigate the effectiveness and safety of treatments such as Eribulin, a non-taxane microtubule inhibitor that is recommended for use beyond second-line therapy.
Methods: This retrospective multicenter study assessed 105 patients with HER2-negative advanced breast cancer who received Eribulin treatment from 2020 to 2023.
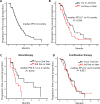
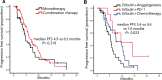
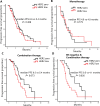
Results: With a median follow-up of 13.3 months, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 6.0 months. Patients on early-line Eribulin had a significantly longer PFS (6.7 vs. 4.9 months, P = 0.038) than those on later lines. Combination therapy tended toward longer PFS than monotherapy (6.4 vs. 4.9 months; P = 0.319), albeit non-significantly. Combinations with PD-1 inhibitors or chemotherapy had a higher PFS than those with anti-angiogenic agents (P = 0.022). Among ER-negative patients in the combination therapy subgroup, HER2-zero tumors had a significantly longer PFS than HER2-low tumors (9.5 vs. 4.1 months, P = 0.026). The most frequently observed adverse events were hematological toxicity, with the majority classified as manageable in severity.
Conclusion: The findings emphasize the potential of Eribulin in the treatment of HER2-negative advanced breast cancer, highlighting the need for further large-scale, prospective studies to refine and enhance treatment strategies.
Keywords: Eribulin; HER2-low; breast cancer; combination therapy; progression-free survival.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Han, Hu, Xiong, Wang and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(45):iii-iv, ix-221. doi: 10.3310/hta11450. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999840
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
Taxane monotherapy regimens for the treatment of recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 12;7(7):CD008766. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008766.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35866378 Free PMC article.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
-
- Trayes KP, Cokenakes SEH. Breast cancer treatment. Am Fam Physician. (2021) 104:171–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

