Angiotensin II in Catecholamine-Refractory Shock: A Systematic Review and Exploratory Analysis of the Angiotensin II for the Treatment of High-Output Shock (ATHOS-3) Trial
- PMID: 40548153
- PMCID: PMC12182914
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.86546
Angiotensin II in Catecholamine-Refractory Shock: A Systematic Review and Exploratory Analysis of the Angiotensin II for the Treatment of High-Output Shock (ATHOS-3) Trial
Abstract
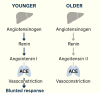
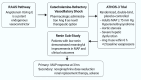
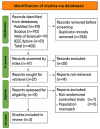
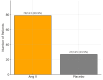
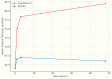
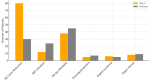
Vasodilatory shock that does not respond to high-dose catecholamine vasopressors remains a life-threatening condition and is characterized by severe hypotension and high mortality. Angiotensin II, a non-catecholamine vasopressor that activates angiotensin type 1 receptors, has emerged as a potential therapeutic agent for restoring vascular tone in this setting. This systematic review aimed to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and hemodynamic effects of intravenous angiotensin II in adult patients with vasodilatory shock unresponsive to catecholamines, with a focus on data from the Angiotensin II for the Treatment of High-Output Shock (ATHOS-3) randomized trial and related studies. Following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2020 guidelines, a systematic search was performed to identify randomized controlled trials and protocol-based investigations involving angiotensin II administration in adult patients with catecholamine-refractory vasodilatory shock. Eligible studies included the ATHOS-3 randomized trial, a renal-focused post hoc analysis, and the DARK-Sepsis protocol. Extracted outcomes included the proportion of patients achieving target mean arterial pressure, changes in catecholamine dose requirements, incidence of renal replacement therapy, and adverse event profiles. Risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2.0 tool. Three studies involving a total of 321 patients were included. In the ATHOS-3 trial, angiotensin II significantly increased mean arterial pressure within 30 minutes. The proportion of patients achieving the target pressure threshold was 69.9% in the angiotensin II group versus 23.4% in the placebo group (P < 0.001). Angiotensin II administration was associated with a reduction in concurrent catecholamine use and a lower rate of renal replacement therapy initiation (19.0% versus 32.4%; P = 0.015). The overall incidence of adverse events, including thromboembolic and ischemic complications, did not differ significantly between groups. Exploratory findings indicated a greater therapeutic response in patients with elevated baseline plasma renin levels. All studies included were rated as low risk of bias. Angiotensin II appears to be a safe and effective adjunct to conventional vasopressor therapy in catecholamine-refractory vasodilatory shock, offering rapid hemodynamic improvement and potential organ protection. The observed reduction in renal replacement therapy initiation and the enhanced response in renin-elevated subgroups warrant further investigation in biomarker-guided clinical trials.
Keywords: angiotensin ii; athos-3; catecholamine-refractory shock; renal replacement therapy; renin-angiotensin system; vasodilatory shock; vasopressor therapy.
Copyright © 2025, Khallikane et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
An index of the initial blood pressure response to angiotensin II treatment and its association with clinical outcomes in vasodilatory shock.Crit Care. 2025 Feb 19;29(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s13054-025-05311-z. Crit Care. 2025. PMID: 39972379 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Topotecan, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride and paclitaxel for second-line or subsequent treatment of advanced ovarian cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Mar;10(9):1-132. iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta10090. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16545208
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The pharmacotherapeutic options in patients with catecholamine-resistant vasodilatory shock. Albertson TE, Chenoweth JA, Lewis JC, Pugashetti JV, Sandrock CE, Morrissey BM. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2022;15:959–976. - PubMed
-
- Angiotensin II for the treatment of vasodilatory shock. Khanna A, English SW, Wang XS, et al. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:419–430. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
