The Nutritarian Women's Health Study (NWHS): Cohort 1
- PMID: 40548235
- PMCID: PMC12177816
- DOI: 10.1177/15598276221135791
The Nutritarian Women's Health Study (NWHS): Cohort 1
Abstract
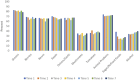
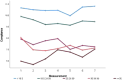
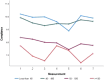
Plant-based dietary patterns are associated with chronic disease risk reduction, prevention, and reversal. As such, the Nutritarian diet is a dietary plan grounded in the daily consumption of micronutrient-dense, plant-rich foods that satisfy nutrient needs with a corresponding improvement in overall health. The Nutritarian Women's Health Study was a fully-online intervention that included supportive, automated email messages, with participants self-reporting dietary adherence and anthropometric measurements quarterly. Changes in Body Mass Index (BMI) were not significant. The groups with the lowest baseline Waist-to-Height-Ratio (WHtR) showed an initial increase followed by a decrease. Responses related to dietary adherence showed that most participants easily consumed greens, beans, onions/garlic, berries, and seeds, avoided animal products, alcohol, and refined foods, but had difficulty with regularly consuming mushrooms and tomatoes. A midpoint questionnaire revealed participants consumed an overwhelming amount of their meals/snacks according to the dietary plan and about half found it easy/very easy to eat strictly Nutritarian. A large majority reported a positive change in health from participating in the study. The barriers to following the dietary plan include a busy lifestyle and the opposing views/pressures from friends, family, co-workers, and/or spouse/partner. It is important to evaluate this fully-online approach when considering future interventions.
Keywords: Nutritarian; Plant-based; dietary adherence; nutrient-dense; plant-rich; virtual-intervention; whole-food.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: Joel Fuhrman, MD, who developed the Nutritarian Diet, is President of the Nutritional Research Foundation, who funded this study, and is a Nutrition Protocol Consultant for this study. Dr. Fuhrman had no role in data collection and analysis, did not have access to the raw data, was not involved in the decision to publish, and had no role in the preparation of this manuscript. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Kimokoti RW, Millen BE. Nutrition for the prevention of chronic diseases. Med Clin North Am. 2016;100(6):1185-1198. - PubMed
-
- Melina V, Craig W, Levin S. Position of the academy of nutrition and dietetics: Vegetarian diets. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2016;116(12):1970-1980. - PubMed
-
- Laster J, Frame LA. Beyond the calories-is the problem in the processing? Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2019;17(4):577-586. - PubMed
-
- Martínez Leo EE, Segura Campos MR. Effect of ultra-processed diet on gut microbiota and thus its role in neurodegenerative diseases. Nutrition. 2020;71:110609. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
