Therapeutic Effects of Naringin on Bisphenol A-Induced Oxidative Stress Damage in Nervous and Reproductive Systems of Cockerel Chickens
- PMID: 40548488
- PMCID: PMC12183602
- DOI: 10.1002/vms3.70322
Therapeutic Effects of Naringin on Bisphenol A-Induced Oxidative Stress Damage in Nervous and Reproductive Systems of Cockerel Chickens
Abstract
Background: Bisphenol A (BPA) is an endocrine-disrupting chemical, and it is mostly used in plastic industries. Naringin is a potent flavonoid that has been reported to possess several beneficial pharmacological properties such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic properties.
Objective: The aim of this study was to determine the protective effect of naringin against the damage induced by BPA in the brain and testes of commercial chicken.
Methods: Thirty-day-old cockerel chickens were purchased and reared for 6 weeks and subsequently divided into six groups: group A (control), group B (100 ppm BPA-treated), group C (BPA and 100 mg/kg naringin-treated), Group D (BPA and 200 mg/kg naringin-treated), group E (100 mg/kg naringin-treated), and group F (200 mg/kg naringin-treated). BPA was administered via drinking water, while naringin was administered via oral gavage. Analyses such as biochemical assays, hormonal assays, histopathology, and immunohistochemistry were done.
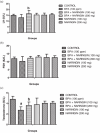
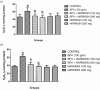
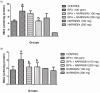
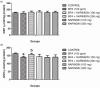
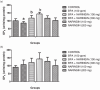
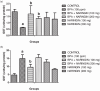
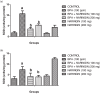
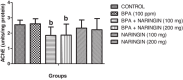
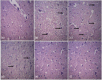
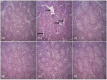
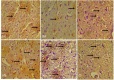
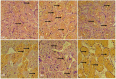
Results: The results showed a decrease in the level of LH, FSH, and testosterone, an increase in the level of oxidative stress markers (MDA and H2O2), and alteration in the levels of enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants (GSH, GST, SOD, GPx) in the brain and testes of the BPA-intoxicated group. Histologically, neuronal necrosis and degeneration were observed in the brain, and degeneration of testicular cells was seen in the testes of BPA-intoxicated chickens. Immunohistochemical evaluation revealed low expression of myelin basic protein in the brain and increased expression of caspase 3 in the testes of the BPA-intoxicated group.
Conclusions: Naringin reversed the neurotoxicity and reproductive toxicity of BPA by normalizing the values of the altered parameters. Hence, naringin ameliorated the deleterious effects caused by BPA in both the brain and testes by enhancing the antioxidant defence mechanism.
Keywords: antioxidant; bisphenol A; chickens; naringin; nervous system; reproductive system.
© 2025 The Author(s). Veterinary Medicine and Science published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Akintunde, J. K. , Akintola T. E., Adenuga G. O., Odugbemi Z. A., Adetoye R. O., and Akintunde O. G.. 2020. “Naringin Attenuates Bisphenol‐A Mediated Neurotoxicity in Hypertensive Rats by Abrogation of Cerebral Nucleotide Depletion, Oxidative Damage and Neuroinflammation.” Neurotoxicology 81: 18–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

