In vitro susceptibility profiles of 16 antifungal drugs against Trichophyton indotineae
- PMID: 40548712
- PMCID: PMC12323362
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.00618-25
In vitro susceptibility profiles of 16 antifungal drugs against Trichophyton indotineae
Abstract
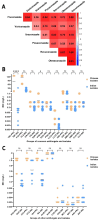
The worldwide emergence of Trichophyton indotineae has garnered significant attention due to its growing resistance to conventional antifungal therapies, posing significant challenges to the effective management of dermatophytosis. The in vitro activities of 16 antifungals were tested against 37 T. indotineae isolates using the broth microdilution method according to Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute protocol M38-A3. Luliconazole and amorolfine exhibited low MICs, while itraconazole showed moderately decreased susceptibility, making them preferred treatment options. Echinocandins demonstrated favourable in vitro activity against T. indotineae, but their potential as therapeutic alternatives for recalcitrant dermatophytosis remains uncertain due to pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic limitations. In contrast, terbinafine, fluconazole, griseofulvin, oteseconazole, isavuconazole, ravuconazole, and amphotericin B exhibited elevated MICs for many strains, with strong correlations between certain azoles, indicating potential cross-resistance. A difference in the susceptibility to terbinafine and voriconazole between Chinese and Indian isolates was observed. These findings could provide valuable insights into antifungal resistance patterns and help guide treatment strategies for T. indotineae infections.
Importance: Trichophyton indotineae is a novel emerging dermatophyte that has rapidly spread globally in recent years. Its resistance to first-line antifungal agents, particularly terbinafine and fluconazole, has significantly limited treatment options, emphasizing the urgent need for alternative therapies. This study provides comprehensive antifungal susceptibility data for 16 available antifungal agents, offering valuable insights into potential treatment strategies.
Keywords: Trichophyton indotineae; amphotericin B; antifungal susceptibility; azoles; echinocandins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A systematic review on the emergence of terbinafine-resistant Trichophyton indotineae in Europe: Time to act?J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025 Feb;39(2):364-376. doi: 10.1111/jdv.20270. Epub 2024 Jul 31. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025. PMID: 39082800
-
Clinical alert: arrival of terbinafine resistant Trichophyton indotineae in New Zealand.N Z Med J. 2025 Feb 28;138(1610):31-38. doi: 10.26635/6965.6815. N Z Med J. 2025. PMID: 40014769
-
Trichophyton indotineae: Epidemiology, antifungal resistance and antifungal stewardship strategies.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025 Jul 4. doi: 10.1111/jdv.20810. Online ahead of print. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025. PMID: 40613321 Review.
-
Mapping the Global Spread of T. indotineae: An Update on Antifungal Resistance, Mutations, and Strategies for Effective Management.Mycopathologia. 2024 May 11;189(3):45. doi: 10.1007/s11046-024-00856-z. Mycopathologia. 2024. PMID: 38734753
-
Whole Genome Sequence Analysis of Terbinafine Resistant and Susceptible Trichophyton Isolates from Human and Animal Origin.Mycopathologia. 2025 Jan 9;190(1):13. doi: 10.1007/s11046-024-00920-8. Mycopathologia. 2025. PMID: 39789248
References
-
- Ebert A, Monod M, Salamin K, Burmester A, Uhrlaß S, Wiegand C, Hipler U-C, Krüger C, Koch D, Wittig F, Verma SB, Singal A, Gupta S, Vasani R, Saraswat A, Madhu R, Panda S, Das A, Kura MM, Kumar A, Poojary S, Schirm S, Gräser Y, Paasch U, Nenoff P. 2020. Alarming India-wide phenomenon of antifungal resistance in dermatophytes: a multicentre study. Mycoses 63:717–728. doi: 10.1111/myc.13091 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

