High-Reliability Thermoreceptors with Minimal Temporal and Spatial Variations Through Photo-Induced Patterning Thermoelectrics
- PMID: 40549060
- PMCID: PMC12185834
- DOI: 10.1007/s40820-025-01821-1
High-Reliability Thermoreceptors with Minimal Temporal and Spatial Variations Through Photo-Induced Patterning Thermoelectrics
Abstract
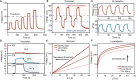
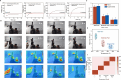
The development of bionic sensing devices with advanced physiological functionalities has attracted significant attention in flexible electronics. In this study, we innovatively develop an air-stable photo-induced n-type dopant and a sophisticated photo-induced patterning technology to construct high-resolution joint-free p-n integrated thermoelectric devices. The exceptional stability of the photo-induced n-type dopant, combined with our meticulously engineered joint-free device architecture, results in extremely low temporal and spatial variations. These minimized variations, coupled with superior linearity, position our devices as viable candidates for artificial thermoreceptors capable of sensing external thermal noxious stimuli. By integrating them into a robotic arm with a pain perception system, we demonstrate accurate pain responses to external thermal stimuli. The system accurately discerns pain levels and initiates appropriate protective actions across varying intensities. Our findings present a novel strategy for constructing high-resolution thermoelectric sensing devices toward precise biomimetic thermoreceptors.
Keywords: Artificial thermoreceptors; Sensors; Thermoelectric composites; Wearable electronics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no interest conflict. They have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. Guangming Chen and Jun Chen are editorial board members for Nano-Micro Letters and were not involved in the editorial review or the decision to publish this article. All authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
All-3D-Printed PEDOT:PSS-Based Stretchable Thermoelectric Devices for Power Generation.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 Jul 16;17(28):40836-40844. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5c03781. Epub 2025 Jul 1. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 40590897
-
A Flexible Smart Healthcare Platform Conjugated with Artificial Epidermis Assembled by Three-Dimensionally Conductive MOF Network for Gas and Pressure Sensing.Nanomicro Lett. 2024 Oct 25;17(1):50. doi: 10.1007/s40820-024-01548-5. Nanomicro Lett. 2024. PMID: 39453552 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Reading aids for adults with low vision.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 17;4(4):CD003303. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003303.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29664159 Free PMC article.
-
The Lived Experience of Autistic Adults in Employment: A Systematic Search and Synthesis.Autism Adulthood. 2024 Dec 2;6(4):495-509. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0114. eCollection 2024 Dec. Autism Adulthood. 2024. PMID: 40018061 Review.
References
-
- S. Wang, J. Xu, W. Wang, G.N. Wang, R. Rastak et al., Skin electronics from scalable fabrication of an intrinsically stretchable transistor array. Nature 555(7694), 83–88 (2018). 10.1038/nature25494 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
