Engineering saline-alkali-tolerant apple rootstock by knocking down MdGH3 genes in M9-T337
- PMID: 40549263
- PMCID: PMC12185813
- DOI: 10.1007/s44154-025-00236-7
Engineering saline-alkali-tolerant apple rootstock by knocking down MdGH3 genes in M9-T337
Abstract
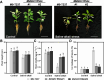
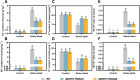
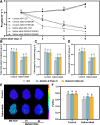
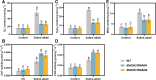
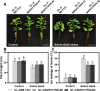
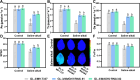
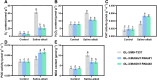
Soil salinization and alkalization have become an increasingly severe global issues, significantly limiting both the yield and quality of apples (Malus × domestica). M9-T337 is a widely used apple dwarfing rootstock; however, it is sensitive to saline-alkali stress. Therefore, developing saline-alkali tolerant apple rootstocks is essential. In this study, we utilized RNAi (RNA interference) technology to knock down GH3 genes in the M9-T337 background, aiming to engineer a dwarfing and stress-tolerant apple rootstock. We found that MdGH3 RNAi plants exhibited superior morphology compared to M9-T337 under saline-alkali stress conditions, characterized by more robust root systems, increased plant height, a lower Na+/K+ ratio, and enhanced photosynthetic and antioxidant capacities. Moreover, when MdGH3 RNAi plants were used as rootstocks, the GL-3/MdGH3 RNAi plants also displayed greater plant height, root vitality, photosynthetic ability, and antioxidant capacity compared to GL-3 grafted onto M9-T337 rootstock. Taken together, our study constructed a saline-alkali-tolerant apple rootstock by knocking down MdGH3 genes.
Keywords: MdGH3 RNAi; Apple; M9-T337; Rootstock; Saline-alkali stress.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All authors consent to participate. Consent for publication: All authors consent for publication. Competing interests: Q.G. is a member of the editorial board but was not involved in the journal's review, or any decisions, related to this submission.
Figures
References
-
- Chang S, Puryear J, Cairney J (1993) A simple and efficient method for isolating RNA from pine trees. Plant Mol Biol Report 11(2):113–116. 10.1007/BF02670468 - DOI
-
- Chen C, He G, Li J, Perez-Hormaeche J, Becker T, Luo M, Wallrad L, Gao J, Li J, Pardo JM, Kudla J, and Guo Y (2023) A salt stress-activated GSO1-SOS2-SOS1 module protects the Arabidopsis root stem cell niche by enhancing sodium ion extrusion. EMBO J 42(13):e113004. 10.15252/embj.2022113004 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cimen B, Yesiloglu T (2016) Rootstock breeding for abiotic stress tolerance in citrus. In: Abiotic and biotic stress in plants - recent advances and future perspectives. IntechOpen. 10.5772/62047
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

