Relationship Between Stroke Knowledge, Health Information Literacy, and Health Self- Management Among Patients with Stroke: Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 40549967
- PMCID: PMC12208508
- DOI: 10.2196/63956
Relationship Between Stroke Knowledge, Health Information Literacy, and Health Self- Management Among Patients with Stroke: Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study
Erratum in
- doi: 10.2196/80547
Abstract
Background: The World Health Organization highlights the essential role of effective self-management in the prevention and control of chronic diseases, noting that proper self-management can significantly slow disease progression. Stroke, which ranks as the third leading cause of death worldwide, is often accompanied by inadequate self-management among patients. While health information literacy (HIL) has been shown to influence self-management in conditions such as diabetes and hypertension, its role as a mediating factor linking disease perception and health behavior in patients with stroke remains insufficiently explored. Addressing this research gap is vital for developing targeted interventions.
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the current status of HIL, stroke knowledge, and self-management abilities among patients with stroke in Southwest China. Additionally, the study analyzed the relationships among these three factors and their mechanisms of action, providing evidence to inform the development of effective health education strategies for enhancing self-management in patients with stroke.
Methods: A multicenter cross-sectional design was employed, enrolling 514 patients with stroke from the neurology departments of three tertiary general hospitals in Chengdu between September 2022 and March 2023. Data collection used a standardized set of scales: the health information literacy questionnaire for stroke assessed HIL, the stroke prevention questionnaire evaluated knowledge levels, and the stroke self-management assessment scale measured self-management abilities. Regression analysis and bootstrap mediation effect testing were conducted using SPSS software (version 26.0).
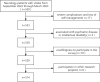
Results: Patients with stroke had a mean (SD) score of 17.61 (6.46) for stroke knowledge, 61.17 (13.58) for HIL, and 158.70 (19.07) for self-management skills. Correlation analysis indicated a positive correlation of stroke knowledge with both self-management (r=0.668; P<.001) and HIL (r=0.138; P<.001). The mediation test showed a significant mediating effect of HIL between stroke knowledge and self-management (β=0.543; 95% CI: 0.431-0.663), with an effect share of 82.77%.
Conclusions: There is a correlation between HIL and self-management; the higher the HIL, the better is the self-management behavior. Furthermore, HIL partially mediates the effect of stroke knowledge on self-management.
Keywords: health information literacy; mediating effect; self-management; stroke; stroke knowledge.
© Mengxue Zeng, Yanhua Liu, Ying He, Wenxia Huang. Originally published in JMIR Medical Informatics (https://medinform.jmir.org).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Computer and mobile technology interventions for self-management in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 23;5(5):CD011425. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011425.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28535331 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Exercise interventions and patient beliefs for people with hip, knee or hip and knee osteoarthritis: a mixed methods review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 17;4(4):CD010842. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010842.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29664187 Free PMC article.
-
Latent Profile Analysis of Health Information Literacy in COPD Patients and Its Association with Quality of Life.COPD. 2025 Dec;22(1):2548422. doi: 10.1080/15412555.2025.2548422. Epub 2025 Aug 27. COPD. 2025. PMID: 40859762
References
-
- Bisaillon S, Douen A, Neabel B, Pageau N, Selchen D. Saving costs using an ounce of prevention: introduction of a regional stroke prevention clinic. Axone. 2006;27(3):29–33. Medline. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous