Surgical resection of vascular-invasive late-stage hepatocellular carcinoma following transarterial chemoembolization combined with lenvatinib and tislelizumab: Two case reports and literature review
- PMID: 40550061
- PMCID: PMC12187305
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042973
Surgical resection of vascular-invasive late-stage hepatocellular carcinoma following transarterial chemoembolization combined with lenvatinib and tislelizumab: Two case reports and literature review
Abstract
Rationale: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with hepatic vein invasion poses significant treatment challenges and is associated with poor prognosis. Recent studies suggest that a combination of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), targeted therapy, and immunotherapy may downstage advanced tumors, making surgical resection possible.
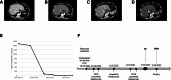
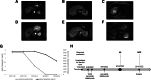
Patient concerns: A 61-year-old female presented with a 3.7 × 3.1 cm hepatic mass invading the hepatic veins. A 75-year-old male exhibited a 6.7 × 5.1 cm liver tumor involving the right hepatic vein.
Diagnoses: Both patients were diagnosed with advanced HCC with vascular invasion, confirmed by contrast-enhanced imaging and elevated alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels.
Interventions: In case 1, the patient received 2 rounds of TACE and 3 cycles of lenvatinib plus tislelizumab. In case 2, the patient underwent 1 TACE session and 2 cycles of the same combination therapy. Both cases showed significant tumor shrinkage, allowing subsequent R0 surgical resection.
Outcomes: Pathological evaluation following surgery revealed a major pathological response in both patients. Postoperative recovery was uneventful, and both patients remained disease-free during follow-up.
Lessons: The combination of TACE, lenvatinib, and tislelizumab may offer an effective multimodal strategy for converting unresectable HCC with vascular invasion into resectable disease, potentially improving long-term outcomes.
Keywords: HCC; TACE; gallbladder; hepatic vein; immunohistochemistry; immunotherapy; lenvatinib; liver metastasis.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Lyu N, Kong Y, Mu L, et al. Hepatic arterial infusion of oxaliplatin plus fluorouracil/leucovorin vs. sorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2018;69:60–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

