Molecular insights into gender-specific differences in rheumatoid arthritis: A study using high-throughput sequencing and Mendelian randomization
- PMID: 40550064
- PMCID: PMC12187339
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042960
Molecular insights into gender-specific differences in rheumatoid arthritis: A study using high-throughput sequencing and Mendelian randomization
Abstract
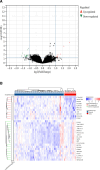
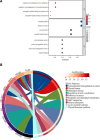
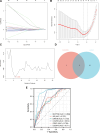
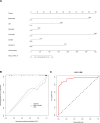
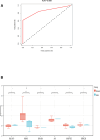
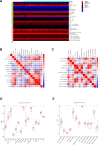
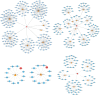
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a multifaceted autoimmune disorder with notable gender differences. The impact of gender-specific genetic variations on RA's pathogenesis remains unclear. This research investigates gender-specific genes in RA using Mendelian randomization (MR) and transcriptome sequencing to understand RA mechanisms, focusing on gender-specific immune responses. We used the limma package to analyze gender-differential genes in RA patients, followed by Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analyses. Key genes were identified through least absolute shrinkage and selection operator and support vector machine recursive feature elimination, and a diagnostic nomogram was constructed and validated using the gene expression omnibus database. Immune cell and function analyses were performed using single-sample gene set enrichment analysis, and a competing endogenous ribonucleic acid (RNA) network was constructed. MR analysis was used to investigate the causal relationship between gender-differential genes and RA. Thirty differentially expressed genes were identified, with Gene Ontology analysis indicating their involvement in neutrophil-mediated killing. Six key genes (MAP7D2, AR, DNAH6, CXorf36, ORM1, and IQGAP3) were identified, and a diagnostic nomogram was developed (area under the curve: 0.956 in the training set, 0.859 in the validation set GSE68689). Furthermore, single-sample gene set enrichment analysis analysis indicated higher immune cell infiltration in female RA patients, highlighting gender's influence on immune response. The competing endogenous RNA network revealed potential RNA regulatory pathways. MR analysis found that the RETN gene has a specific role in seronegative RA patients, particularly in females. This study enhances the understanding of RA's gender-specific pathogenesis and offers a foundation for future personalized treatment and prevention strategies, aiding in developing more effective individualized treatment plans for RA patients.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; ceRNA; gender differences; machine learning; rheumatoid arthritis; transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Machine learning and bioinformatics analysis to identify and validate diagnostic model associated with immune infiltration in rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jul;44(7):2683-2694. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07514-9. Epub 2025 Jun 11. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40500570
-
Identification and validation of CKAP2 as a novel biomarker in the development and progression of rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 25;16:1606201. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1606201. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40636121 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated approach of machine learning, Mendelian randomization and experimental validation for biomarker discovery in diabetic nephropathy.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024 Dec;26(12):5646-5660. doi: 10.1111/dom.15933. Epub 2024 Oct 6. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024. PMID: 39370621
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Biologics or tofacitinib for people with rheumatoid arthritis naive to methotrexate: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 8;5(5):CD012657. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012657. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28481462 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chronic Disease Management Group of Special Committee on Rheumatology and Immunology of Cross-Straits Medicine Exchange Association. Expert recommendations for the chronic disease management of rheumatic arthritis. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2023;62:1256–65. - PubMed
-
- Tian XP, Li MT, Zeng XF. The challenges and opportunities for the management of rheumatoid arthritis in China: an annual report of 2019. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2021;60:593–8. - PubMed
-
- Fang LK, Huang CH, Xie Y, et al. Practice guidelines for patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2020;59:772–80. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

