Diagnosis of Cushing's syndrome with generalized linear model and development of mobile application
- PMID: 40550094
- PMCID: PMC12187266
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042910
Diagnosis of Cushing's syndrome with generalized linear model and development of mobile application
Abstract
Background: Cushing syndrome (CS) is a rare endocrine disorder characterized by excessive secretion of glucocorticoids, leading to a variety of clinical manifestations, comorbidities, and increased mortality despite treatment. Despite advances in imaging modalities and biochemical testing, the diagnosis and management of CS remains challenging. Several tests are used to confirm the diagnosis of CS, including urinary free cortisol measurements, dexamethasone suppression tests (1 mg, 2 mg, and 8 mg), and nocturnal salivary cortisol measurements. However, each of these tests has some limitations, making the diagnosis of CS.
Methods: In this paper, we explore the potential of state-of-the-art machine learning algorithms as a clinical decision support system for analyzing and classifying CS. Our aim is to use advanced machine learning methods to analyze the accuracy rates of diagnostic tests and identify the most sensitive tests for diagnosing CS.
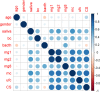
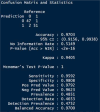
Results: In this study, we performed binary classification based on data from 278 patients with CS (CS+) and 220 healthy patients (CS-). We developed a linear mathematical model with high predictive ability, achieving a classification accuracy of 97.03% and a Kappa value of 94.05%. The correlation graph shows that CS has strong positive relationships with 2 mg (78.8%), 1 mg (76.9%), and mc (72.1%), and moderate positive correlations with 8 mg (45%) and saliva (45.4%). In contrast, gender has almost no correlation with CS, so it was removed from the dataset. As a result, the model achieves an overall classification accuracy of 97.03%. Finally, we converted the linear model into a mobile application for use by specialist doctors in the field of endocrinology.
Conclusion: Traditional diagnostic methods can be time-consuming and require specialized medical expertise. Recently, advances in machine learning and mobile technology have opened new avenues for improving diagnostic accuracy and accessibility. This study explores the integration of machine learning algorithms into a mobile application designed to assist healthcare professionals and patients in the diagnosis of CS.
Keywords: Cushing Diagnosis Mobile App; Cushing disease; Cushing syndrome; ectopic Cushing syndrome; machine learning.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
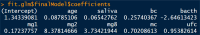
Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does the Presence of Missing Data Affect the Performance of the SORG Machine-learning Algorithm for Patients With Spinal Metastasis? Development of an Internet Application Algorithm.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Jan 1;482(1):143-157. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002706. Epub 2023 Jun 12. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 37306629 Free PMC article.
-
Are Current Survival Prediction Tools Useful When Treating Subsequent Skeletal-related Events From Bone Metastases?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Sep 1;482(9):1710-1721. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003030. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 38517402
-
Emerging diagnostic methods and imaging modalities in cushing's syndrome.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 25;14:1230447. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1230447. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37560300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of self-administered survey questionnaire responses collected using mobile apps versus other methods.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jul 27;2015(7):MR000042. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000042.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26212714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gadelha M, Gatto F, Wildemberg LE, Fleseriu M. Cushing’s syndrome. Lancet. 2023;402:2237–52. - PubMed
-
- Balomenaki M, Margaritopoulos D, Vassiliadi DA, Tsagarakis S. Diagnostic workup of Cushing’s syndrome. J Neuroendocrinol. 2022;34:e13111. - PubMed
-
- Lindholm J, Juul S, Jorgensen JO, et al. Incidence and late prognosis of cushing’s syndrome: a population-based study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:117–23. - PubMed
-
- Wengander S, Trimpou P, Papakokkinou E, Ragnarsson O. The incidence of endogenous Cushing’s syndrome in the modern era. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2019;91:263–70. - PubMed
-
- Cushing H. The Pituitary Body and its Disorders: Clinical States Produced by Disorders of the Hypophysis Cerebri. J.B. Lippincott Company; 1912.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

