Elevated soluble CD226 in Takayasu arteritis is useful for differentiation from giant cell arteritis, disease activity assessment, and prognosis prediction
- PMID: 40550099
- PMCID: PMC12187342
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042844
Elevated soluble CD226 in Takayasu arteritis is useful for differentiation from giant cell arteritis, disease activity assessment, and prognosis prediction
Abstract
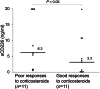
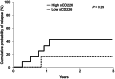
Takayasu arteritis (TAK) is characterized by vascular injury, in which endothelial cells and immune cells including natural killer cells, have key roles. CD226 is an activating receptor expressed on natural killer cells and T cells, and the soluble form of CD226 (sCD226) is increased in diseases involving these cells. Therefore, we investigated the utility of serum sCD226 as a biomarker for TAK. Serum sCD226 levels were measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in 34 TAK patients and 21 giant cell arteritis (GCA) patients. The associations between sCD226 levels and the angiographic classification, disease activity, and prognosis of TAK were analyzed. Serum sCD226 levels were significantly higher in TAK patients than in GCA patients. In patients with TAK, serum sCD226 levels were significantly elevated in the group of type Ⅴ compared with type Ⅰ to Ⅳ. Serum sCD226 levels were also elevated in patients with active TAK and in those with poor responses to corticosteroids. Moreover, the cumulative probability of relapse was increased in patients with high sCD226 levels. Serum sCD226 levels differentiated TAK from GCA and were associated with disease activity and relapse of TAK. Thus, serum sCD226 might be a useful biomarker for the management of TAK.
Keywords: Takayasu arteritis; biomarkers; disease activity; giant cell arteritis; soluble CD226.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, et al. 2012 Revised International Chapel Hill consensus conference nomenclature of vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Grayson PC, Ponte C, Suppiah R, et al. 2022 American College of Rheumatology/EULAR classification criteria for Takayasu arteritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022;81:1654–60. - PubMed
-
- Ponte C, Grayson PC, Robson JC, et al. 2022 American College of Rheumatology/EULAR classification criteria for giant cell arteritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022;81:1647–53. - PubMed
-
- Kermani TA. Takayasu arteritis and giant cell arteritis: are they a spectrum of the same disease? Int J Rheum Dis. 2019;22(Suppl 1):41–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

