Vacation and back-to-school effect on influenza transmission among school-age children in Guangzhou, China: an ecological study from 2010 to 2023
- PMID: 40550718
- PMCID: PMC12186047
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-096341
Vacation and back-to-school effect on influenza transmission among school-age children in Guangzhou, China: an ecological study from 2010 to 2023
Abstract
Objective: To examine whether influenza transmission risk decreased during summer and winter vacations and increased after vacations and statutory holiday.
Design: An ecological study.
Setting: Guangzhou, Guangdong Province of China.
Participants: A total of 458 343 influenza cases in school-aged children were included, including 160 067 (35.05%) in kindergarten, 223 817 (48.83%) in primary school, 50 053 (10.92%) in middle school and 23 801 (5.19%) in high school.
Data and methods: Data on influenza cases were obtained from the Notifiable Infectious Disease Surveillance System operated by Guangzhou Centre for Disease Control and Prevention. Influenza incidence rate ratio (IRR) by negative binomial regression model was used to analyse the influenza risk of school-age children during/after vacation to before/during breaks.
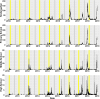
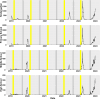
Results: In all four groups, there was significantly lower incidence of influenza during winter and summer vacations compared with the 4 weeks preceding vacations. Compared with the 2 weeks preceding return, kindergarten students experienced the highest influenza risk in the third week after summer vacation (IRR=3.40, 95% CI 2.43to 4.79). Primary school students had the highest risk in the fourth week after winter vacation (IRR=9.59, 95% CI 6.71 to 13.87). Middle school students had the highest risk in the fourth week after summer (IRR=11.60, 95% CI 6.17 to 22.62). High school students also experienced the highest risk in the fourth week following summer (IRR=17.96, 95% CI 8.10 to 42.05). Despite the risk of influenza increasing after returning to school, it remained lower compared with before vacations and holidays.
Conclusions: Due to changes in contact patterns, influenza incidence was high towards the end of term, significantly decreased during vacations and started to rise on returning to school, peaking in the third or fourth week. These findings suggested using holiday periods strategically to promote influenza vaccination and implementing enhanced non-pharmaceutical interventions on students returning to school.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Infection control; Public health; Schools.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Shi J, Xiang N, Zhang Y, et al. Epidemiological characteristics on the clustering nature of pandemic (H1N1) 2009 in China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2012;33:62–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
