Multiscale modeling of drug-induced liver injury from organ to lobule
- PMID: 40550856
- PMCID: PMC12185720
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-025-01736-6
Multiscale modeling of drug-induced liver injury from organ to lobule
Abstract
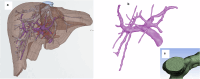
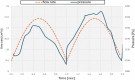
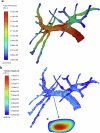
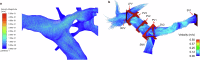
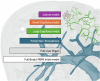
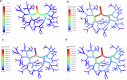
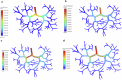
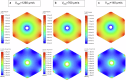
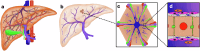
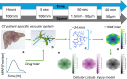
Drug-induced liver injury poses significant challenges in drug development and in clinical care. This study builds on prior work developing a Human Liver Virtual Twin by creating a Multiscale Computational Fluid Dynamics framework that integrates patient-specific anatomical data to predict acetaminophen-induced liver injury as a demonstration of its capability. The model bridges vascular, lobular, and cellular scales to simulate dynamic blood flow, drug transport, and injury mechanisms that accurately reflect clinically observed spatial heterogeneity. Results demonstrate accurate blood flow dynamics, predictions of hepatocellular damage, and a scalable framework for studying spatial heterogeneity applicable to other hepatic pathologies. This work establishes the foundational principles for a whole-organ virtual liver simulation methodology, potentially becoming a powerful tool to guide safety in therapeutic development and clinical treatment strategies, ultimately reducing reliance translation from animal models for preclinical drug testing.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: S.M.L. is a Dassault Systemes employee. J.M.V. is a member of IQDILI and the NIH NIDDK Drug-Induced Liver Injury Network Data Safety and Management Board. N.R.G. has served as a consultant for Dassault Systemes. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Andrade, R. J. et al. Drug-induced liver injury. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim.5, 58 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Ellison, C., Hewitt, M. & Przybylak, K. In Silico Models for Hepatotoxicity. Methods Mol. Biol.2425, 355–392 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Speid, L. H., Lumley, C. E. & Walker, S. R. Harmonization of guidelines for toxicity testing of pharmaceuticals by 1992. Regulatory Toxicol. Pharmacol.12, 179–211 (1990). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

